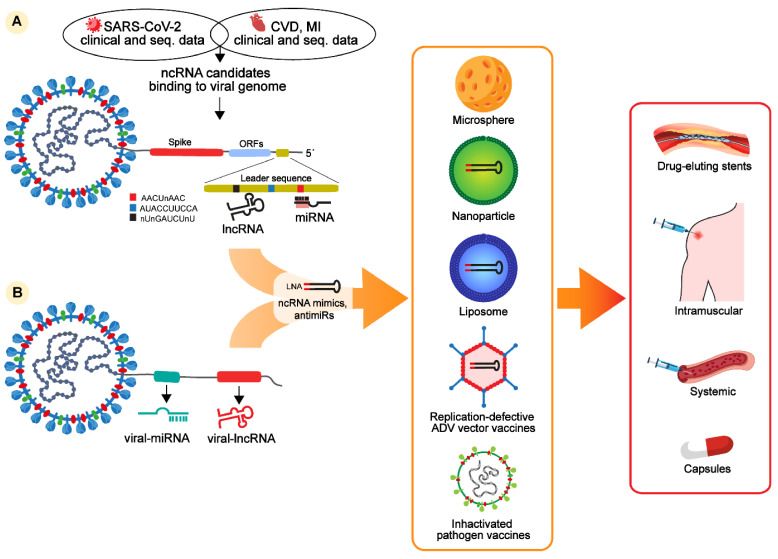
Figure 1.
Host and viral noncoding RNAs and potential therapeutic strategies to treat COVID-19 patients with cardiovascular complications. Noncoding RNA-based therapies derived from (A) clinical and sequencing data from patients with COVID-19, CVD, or MI and from patients with cardiac and COVID-19 diseases indicate that several ncRNAs, such as miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs, are differentially regulated in these patients and contain putative binding sites in the Spike transcript or in the leader sequence of the SARS-CoV-2 genome. Binding specificity might be enhanced for miRNAs binding three motifs conserved in the leader sequence of the SARS-CoV-2 genome, named AACUnAAC, AUACCUUCCA, and nUnGAUCUnU. Potential ncRNAs interacting with the leader sequence can be used to design LNA-oligos mimicking (LNA-RNA mimics) or inhibiting (LNA-anti-miRs) selected ncRNA candidates. (B) Alternatively, recent findings identified the presence of miRNAs and lncRNAs as alternative candidates to design RNA-based inhibitors against viral infection. NcRNA-based mimics or anti-miRs can be encapsulated in microsphere, lipoparticles, or inactivated viral vectors as vaccines to be systemically or intramuscularly delivered. Certain ncRNAs are already in phases I and II of clinical trials as drug-eluting stents. Alternative administrations are in clinical trials, such as modified and stabilized ncRNAs delivered as capsules.