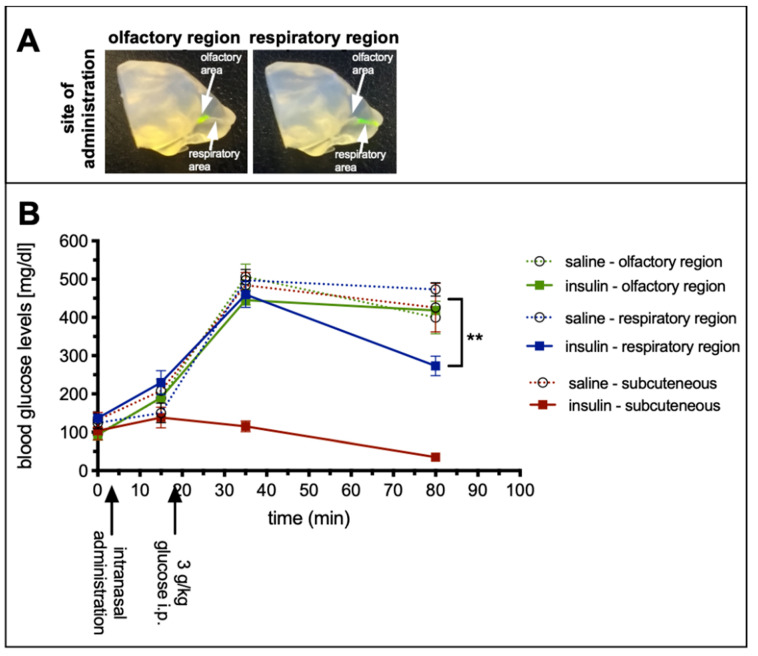
Figure 3.
No peripheral bioactivity after region-specific delivery of insulin detemir to the olfactory region (study 2). Silicone based 3D-model made by vacuum cast method (A), for the visualization of the targeted regions [25]. Adapted with permission from ref. [25]. 2021, Nicole Lange et al. Glucose tolerance test to examine the peripheral effects after region-specific administration of insulin detemir versus vehicle (B), monitored via blood glucose levels. Black arrows highlight catheter-based refined administration to the respiratory or olfactory nasal regions or subcutaneous injections of insulin detemir or vehicle. Mice were challenged with a high dose of intraperitoneal glucose to determine the peripheral activity of insulin detemir. As expected, subcutaneously delivered insulin demonstrated a high peripheral bioactivity by lowering the blood glucose levels. Interestingly, insulin delivered via the respiratory regions covered predominantly with respiratory mucosa was also distributed from the nose to the periphery and displayed 40.2% of the subcutaneously delivered activity. Insulin targeted to the olfactory regions did not show any statistically significant bioactivity in the periphery. Error bars represent mean ± SEM, n = 3. Data were analyzed with two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons. ** p < 0.009. A is reproduced from [25] with kind permission from the rights owner.