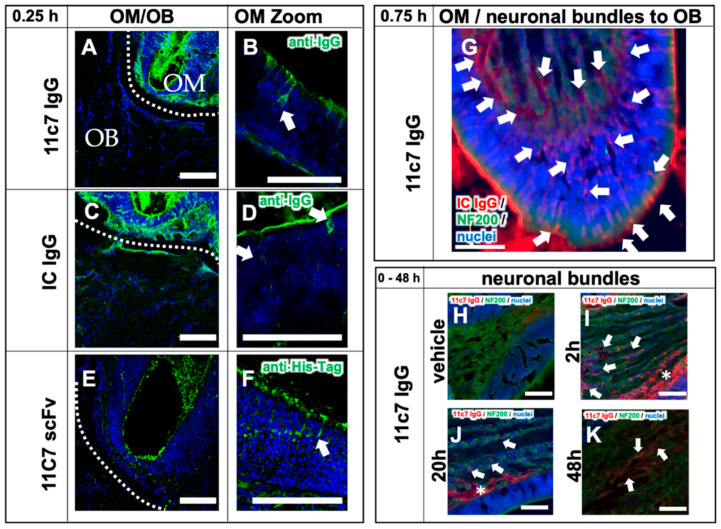
Figure 5.
Transport mechanisms of both the full IgGs 11C7 and the isotype (IC) control, and the 11C7 scFv (study 3). Images from confocal microscopy show the rapid uptake of 11C7 and IC into the olfactory mucosa (OM) and also traces in the olfactory bulb (OB) after only 15 min (A,C). Higher magnification shows evidence for a predominantly intracellular pathway as previously reported from ex vivo olfactory mucosa (see arrowheads) (B,D) [38,39]. In contrast, the 11C7 scFv devoid of an Fc domain appears to be taken up to a lower extent (E) and displays more evidence for a transcellular transport (F). However, it should be noted that IgGs and scFv were visualized with different detections systems (anti-IgG vs. anti-His-Tag) and, hence, the fluorescence intensity should be evaluated with caution. Epiflourescence microscopy demonstrates, 45 min after administration, the full transport scheme with intracellular uptake at the apical mucosa, distribution to the lamina propria and transport along neuronal bundles from the lamina propria to the olfactory bulb (G). For a better visualization, anti-IgG immunoreactivity is displayed here in red, and neurofilament (NF200)-immunoreactivity in green. Transport kinetics along neuronal bundles after a single dose (H–K): while only background is observed in the vehicle control animals (H), decreasing levels of 11C7 are observed within 48 h (I–K). Arrowheads point to distinct stained structures while asterisk show diffuse staining pattern. Scale bar, 100 µm.