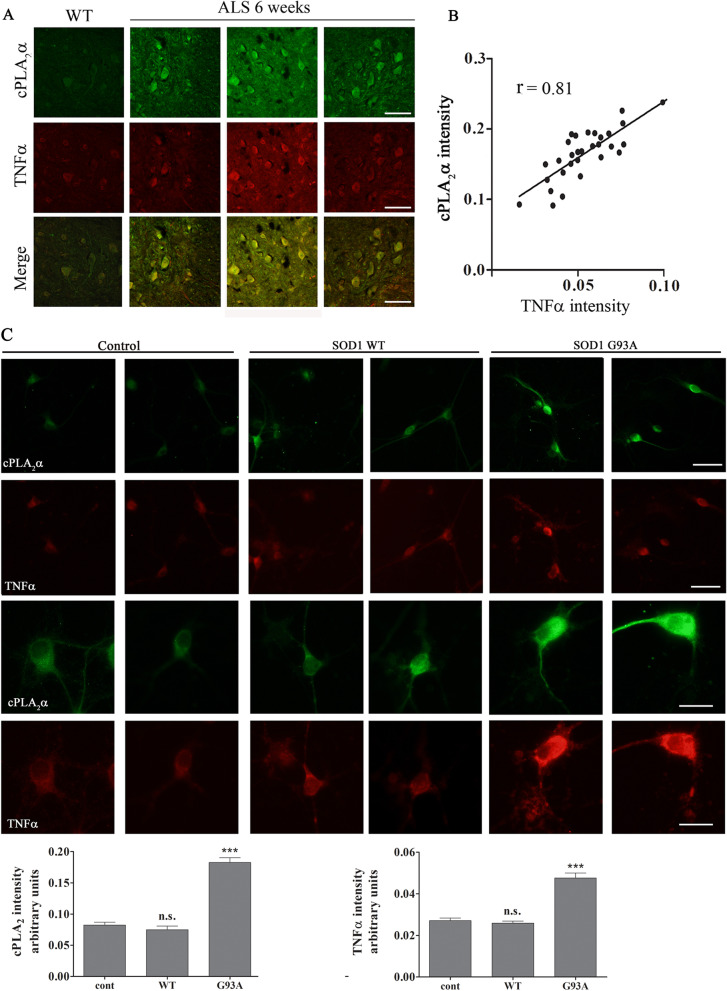
Fig. 6.
Elevated cPLA2α protein expression in the motor neurons is highly correlated with TNFα. A Double immunofluorescence staining of cPLA2α (green) and TNFα (red) proteins in the lumbar spinal cord sections of WT and 6 weeks old mutant SOD1G93A mice. Scale bars = 100 μm. B The Pearson coefficient correlation (r) between cPLA2α and TNFα in the spinal motor neurons of mutant SOD1G93A mice was analyzed. Florescence intensity is expressed in arbitrary units of immunostaining as presented in the representative results in A. Four fields in each of the 8 different mice analyzed. C Elevated cPLA2α and TNFα in primary motor neurons expressing mutant SOD1G93A. Double immunofluorescence staining of cPLA2α (green) and TNFα (red) in primary motor neurons expressing human SOD1WT, mutant SOD1G93A and control cells described in Fig. 3. Two upper panels, scale bars = 50 μm and two lower panels, scale bar s = 20 μm. 3 different independent experiments were analyzed and showed similar results. The means ± SEM fluorescence intensity for cPLA2α and TNFα is presented in the bar graphs as arbitrary units. Five fields in each of the 3 different treatments of motor neurons in each experiment was analyzed. Significance compared to control ***p < 0.001, n.s. non-significant