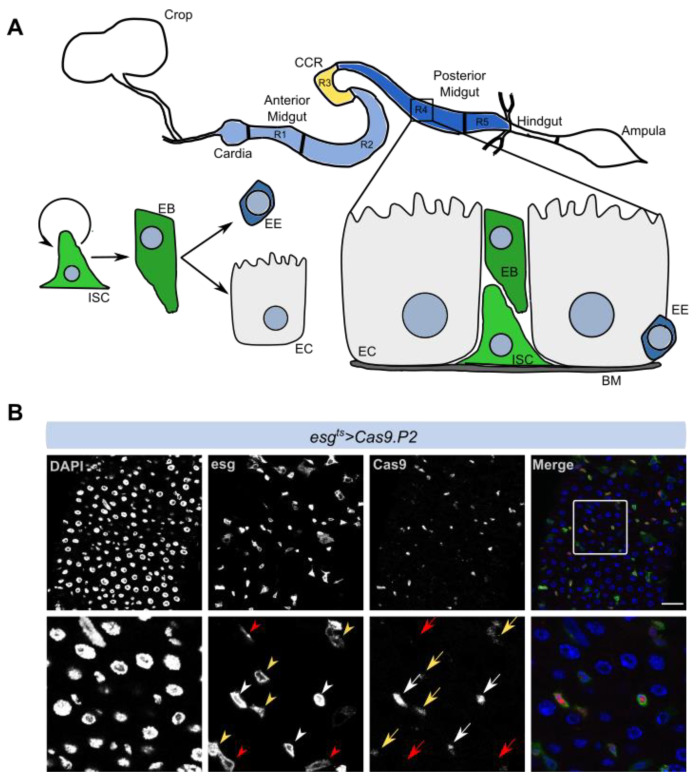
Figure 1.
Digestive tract and intestinal cell types in Drosophila melanogaster. (A) Schematic representation of the intestine, which contains different regions (R1–R5) that house progenitor cells such as intestinal stem cells (ISCs) and enteroblasts (EBs), which can differentiate into enterocytes (ECs) or enteroendocrine cells (EEs). (B) ISCs/EBs are dispersed throughout the midgut and can be marked with escargot (esg > GFP) (arrowheads). Notice that esg > GFP expression is variable (compare white and yellow arrowheads). Expressing Cas9.P2 using the esgts system and staining against Cas9 (Red) reveals that this construct is translated into protein in ISCs/EBs (arrows). Notice that Cas9 expression is variable (compare white and yellow arrows) and some esg > GFP cells lack detectable Cas9 expression (red arrowheads and red arrows). Scale bar: 30 µm.