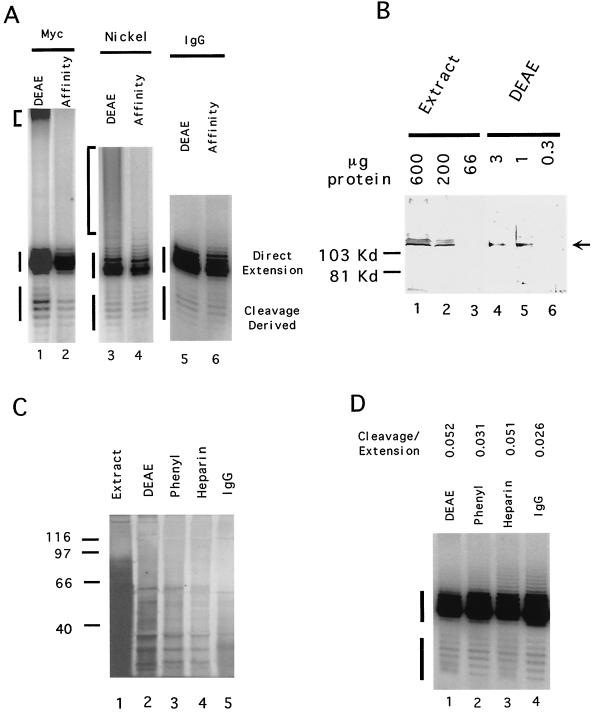
FIG. 3.
Affinity-purified yeast telomerase exhibits a similar cleavage activity as that found in DEAE fractions. (A) Polymerization assays were carried out using OXYT1 (1 μg) as the DNA primer and DEAE fraction (DEAE) or affinity-purified telomerase (Affinity) as the source of telomerase. The affinity resin utilized for each purification is indicated at the top. The amount of protein used for each reaction is as follows: lane 1, 3 μg; lane 2, 45 ng; lane 3, 3 μg of protein; lane 4, 0.4 μg of protein; lane 5, 3 μg of protein; lane 4, ∼0.15 μg of protein. “Direct extension” or “cleavage-derived” products are marked by vertical lines to the left of the panels. Contaminating activity or activities present in the DEAE fraction and responsible for the labeling of high-molecular-weight products (indicated by brackets to the left of the panels) can be removed by the Myc affinity or the nickel affinity chromatographic procedures. (B) Immunoblotting was used to estimate the degree of Est2p enrichment over the DEAE column. Protein A-tagged Est2p from extracts or DEAE fractions was detected using anti-protein A antibodies. The amount of protein loaded is indicated at the top. The location of the protein A-tagged Est2p is indicated by an arrow. (C) Protein compositions of fractions from successive column steps were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and silver staining. The identities and the amounts of the fractions utilized were as follows: lane 1, extract, 30 μg; lane 2, DEAE, 10 μg; lane 3, phenyl, 3 μg; lane 3, heparin, 1.2 μg; lane 4, IgG, ∼0.12 μg. (D) Polymerization assays were carried out using OXYT1 (2 μg) as the DNA primer and fractions from successive column steps. The identities of the fractions used in each reaction were as follows: lane 1, DEAE, 10 μg; lane 2, phenyl, 3 μg; lane 3, heparin, 1.2 μg; lane 4, IgG, ∼0.12 μg. The ratios of cleavage to extension products are listed at the top.