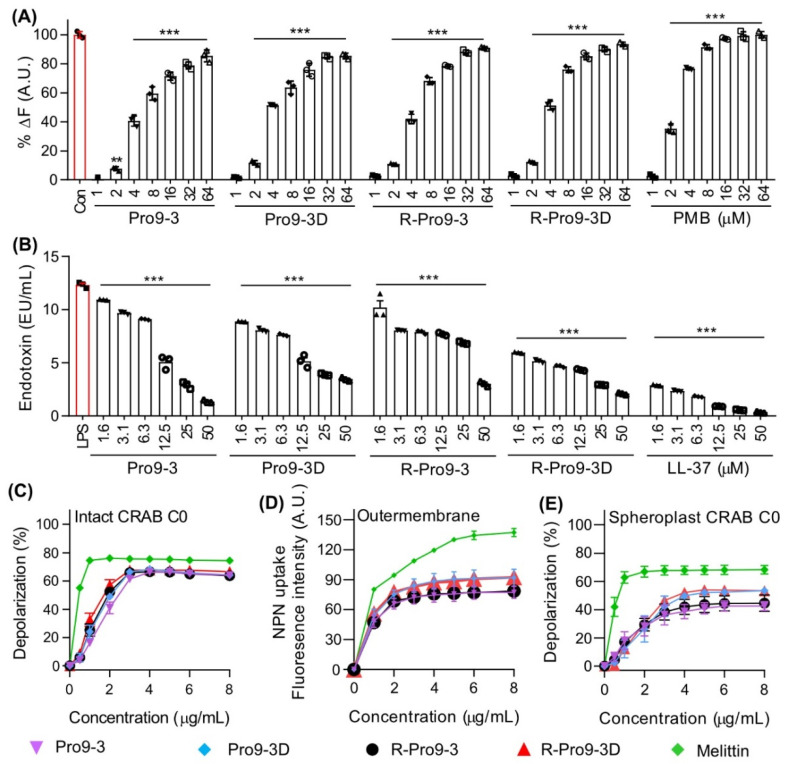
Figure 3.
Antibacterial mechanism of the peptides. (A) Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding affinities peptides based on displacement assays with BODIPY-TR-cadaverine fluorescent dye. (B) Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL) assay showing the LPS neutralization capacities of peptides and LL-37 control. (C) The concentration-dependent depolarization of intact CRAB C0, (D) Outer membrane permeability assessed by NPN uptakes induced by peptides. (E) Cytoplasmic membrane depolarization capacities by peptides on LPS-layer removed spheroplast CRAB C0 cells. Melittin was used as control. Statistical analysis was performed using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s comparison test. The values are expressed as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments and are statistically significant at *** p < 0.001; ns, not significant.