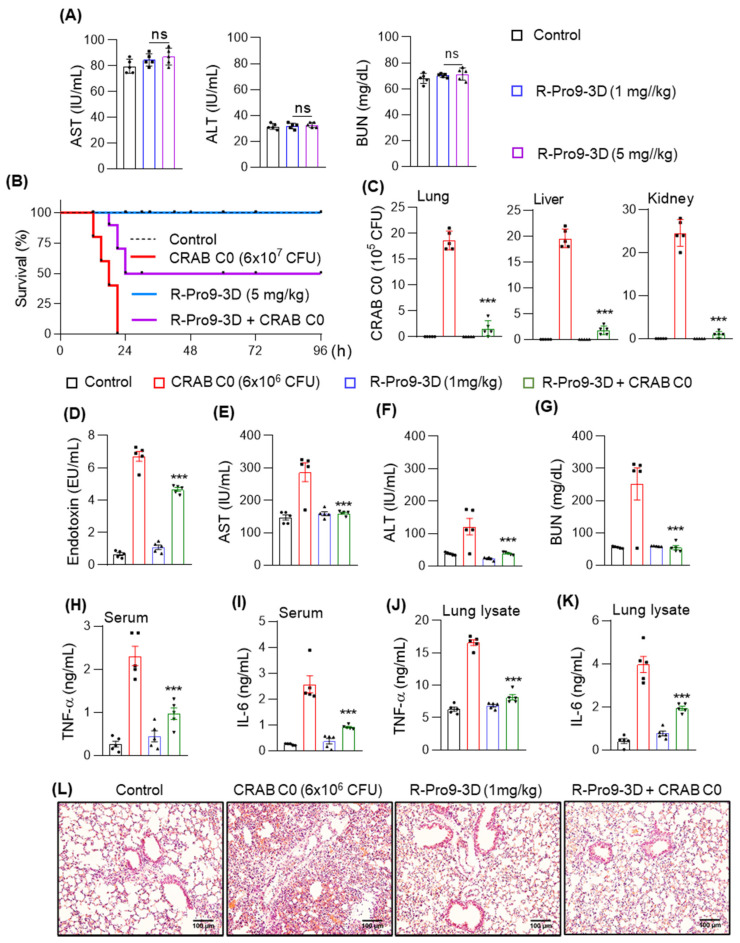
Figure 9.
R-Pro9-3D exhibited antiseptic effects in CRAB C0-induced sepsis mouse model. (A) R-Pro9-3D did not alter the concentrations of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in response to 1 and 5 mg/kg of peptide treatment. Control mice received phosphate-buffered saline only and the treatment was performed for 24 h. (B) R-Pro9-3D prolonged the survival rate of mice infected with CRAB C0. ICR mice (10 per group) were intraperitoneally injected with R-Pro9-3D (5 mg/kg) for 1 h followed by CRAB C0 infection (6 × 107 CFU/mouse) and survival effects were observed for 96 h. In sepsis model, mice (5 mice per group) were treated with R-Pro9-3D (1 mg/kg) for 1 h and the antiseptic analyses were evaluated after CRAB C0 (6 × 106 CFU/mouse, 16 h) infection. (C) R-Pro9-3D restricted the bacterial entry in the lung, liver, and kidneys. The corresponding organ lysates were plated onto agar plates and the total no of bacterial colonies were scored. (D) R-Pro9-3D effectively normalized the endotoxin levels in CRAB C0-infected mice. (E–G) Effect of R-Pro9-3D on serum levels of AST, ALT and BUN. (H–K) R-Pro9-3D inhibited the production of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) in the serum and lung lysates of CRAB C0-infected mice, as measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). (L) Photomicrograph show the modulatory effect of R-Pro9-3D on neutrophil infiltration in the hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained lung tissues (Magnification 20×, Scale bar 100 μm). Statistics was performed using (A,C–K) one-way analysis of variance followed by Dunnett’s test and (B) Kaplan–Meyer test. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (Five mice per group). Comparisons—*** p < 0.001, and ns, non-significant vs. CRAB C0 control.