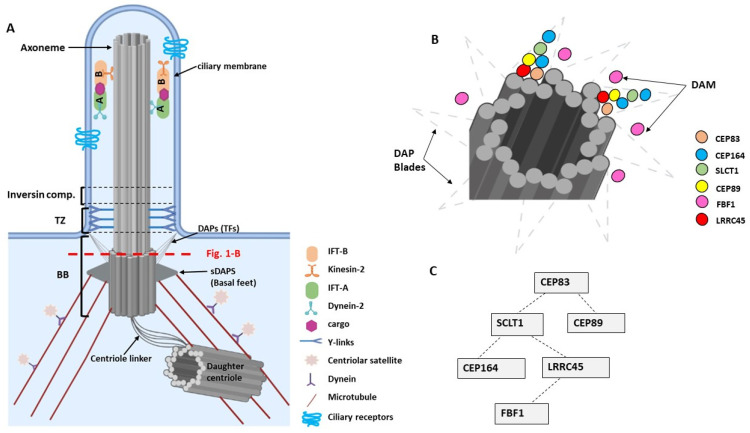
Figure 1.
(A). Basic structures of a primary cilium. The base of the cilium is composed of a basal body (BB), a transition zone (TZ), and the inversin compartment. The BB consists of a modified mother centriole that is linked to microtubules via subdistal appendages (sDAPs) and that is tethered to the plasma membrane via distal appendages (DAPs) and transition fibers (TFs). The non-continuous red line indicates the section of the centriole at the level of the DAPs that is shown in Figure 1B. (B). Schematic diagram showing the arrangement of DAPs as DAP blades comprise CEP83, CEP164, SLCT1, CEP89, and LRRC45 proteins, and the DAP matrix (DAM) includes the FBF1 protein [16]. (C). Hierarchy of assembly of the DAPs at the base of the centriole (adapted from [15,18]). Image was created by BioRender.