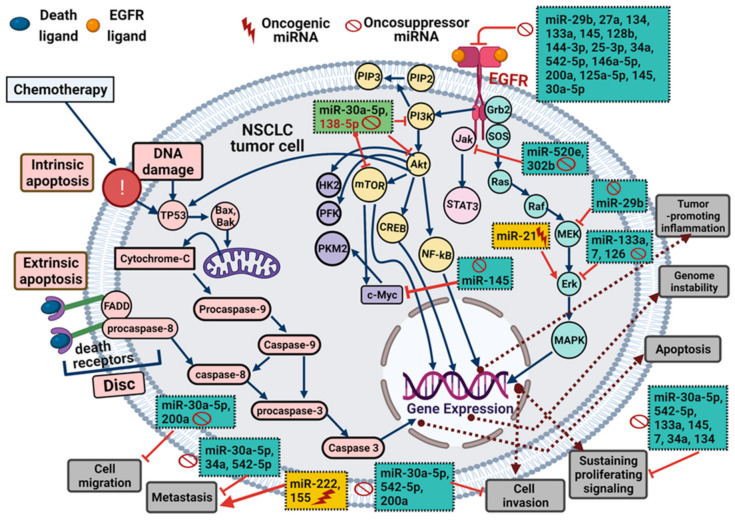
Figure 1.
EGFR signaling components are affected by various miRNAs (oncogenic or tumor suppressors) in non-small cell lung cancer. Activation of the EGFR signaling pathway, including PI3K/Akt, Ras/Raf/MAPK, and Jak/STAT, stimulates inflammation, proliferative signaling, migration, angiogenesis, and invasion. These signaling pathways are controlled by different miRNAs. Binding of death ligand (e.g., TRAIL) to death receptor leads to FADD (adaptor molecule). Pro-caspase-8 activation takes place upon its binding to FADD and DISC formation (extrinsic apoptosis). Chemotherapeutic drugs, such as cisplatin, cause DNA damage and results in p53 activation (intrinsic apoptosis). Activated caspase-8 directly activates other caspases that translocate to the mitochondria promoting the Bax-Bak assembly, thus changing mitochondrial membrane permeability. Cytochrome c is then released into cytosol resulting in caspases activation leading to apoptosis. Several oncogenic and tumor suppressor miRNAs control EGFR signaling components and subsequently affect tumor growth and progression. Blue and red arrows for stimulation, dashed brown arrows for cellular effect, and red “T” for inhibition.