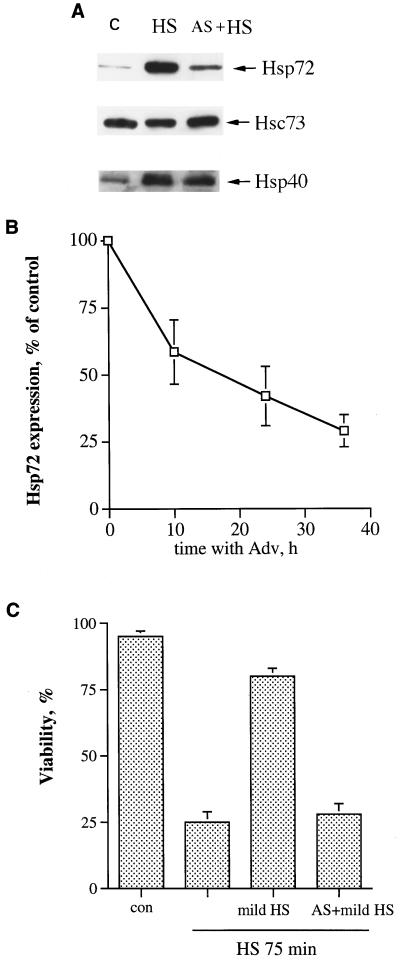
FIG. 1.
Prevention of heat-induced Hsp72 accumulation abolishes acquired thermotolerance in fibroblasts. (A) Expression of Hsp72 antisense RNA prevents heat-induced accumulation of Hsp72 but not that of other Hsps. IMR90 human fibroblasts were infected with an adenovirus expressing Hsp72 antisense RNA (AS) and 36 h after infection were subjected to mild heat shock (45°C, 30 min), followed by recovery for 16 h at 37°C. The levels of Hsp72, Hsc73, and Hsp40 were then assayed by immunoblotting with corresponding antibodies. C, control cells; HS, cells incubated with tetracycline (doxycycline, 1 μg/ml) and exposed to heat shock; AS + HS, cells incubated without tetracycline and exposed to heat shock. (B) Time course of suppression of heat-induced Hsp72 accumulation by the Hsp72 antisense-RNA-expressing adenovirus. Fibroblasts were infected with the Hsp72 antisense-RNA-expressing adenovirus as explained for panel A and were incubated without tetracycline; at various times after infection, they were subjected to mild heat shock with recovery as explained for panel A, and the level of Hsp72 was measured by immunoblotting. The data shown are the means ± standard deviations of three replicates. Adv, adenovirus. (C) Prevention of Hsp72 accumulation by antisense-RNA-expressing adenovirus blocks the acquisition of thermotolerance. Fibroblasts infected with Hsp72 antisense-RNA-expressing adenovirus and pretreated with mild heat shock as explained for panel A were exposed to severe heat shock (45°C, 75 min), and cell viability was assayed 24 h later by acridine orange-ethidium bromide staining. con, control.