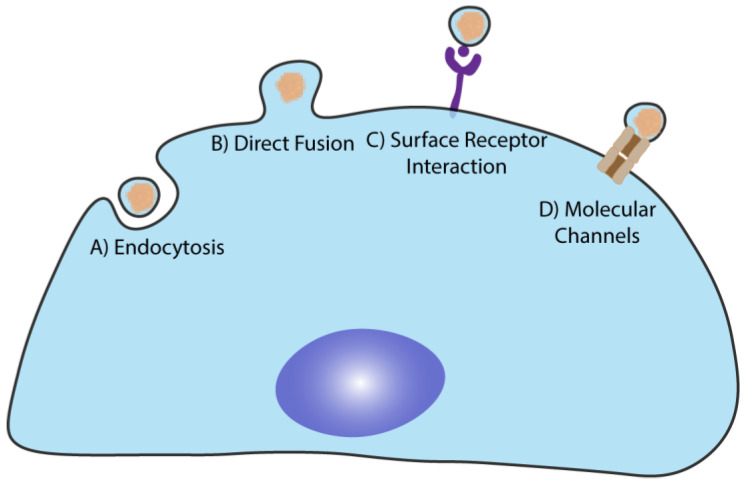
Figure 4.
Cellular uptake pathways for extracellular vesicles (EVs). (A) EVs can be internalized by endocytosis, which is believed to be the main uptake pathway. EVs can also be internalized by (B) direct fusion with the plasma membrane of the target cell releasing their cargo into the lumen. (C) EVs can interact with the target cells without being internalized via surface receptor interaction and activation of signaling pathways. Finally, (D) the presence of molecular channels in EVs, such as connexin 43, may also promote the loading of the luminal cargo to target cells.