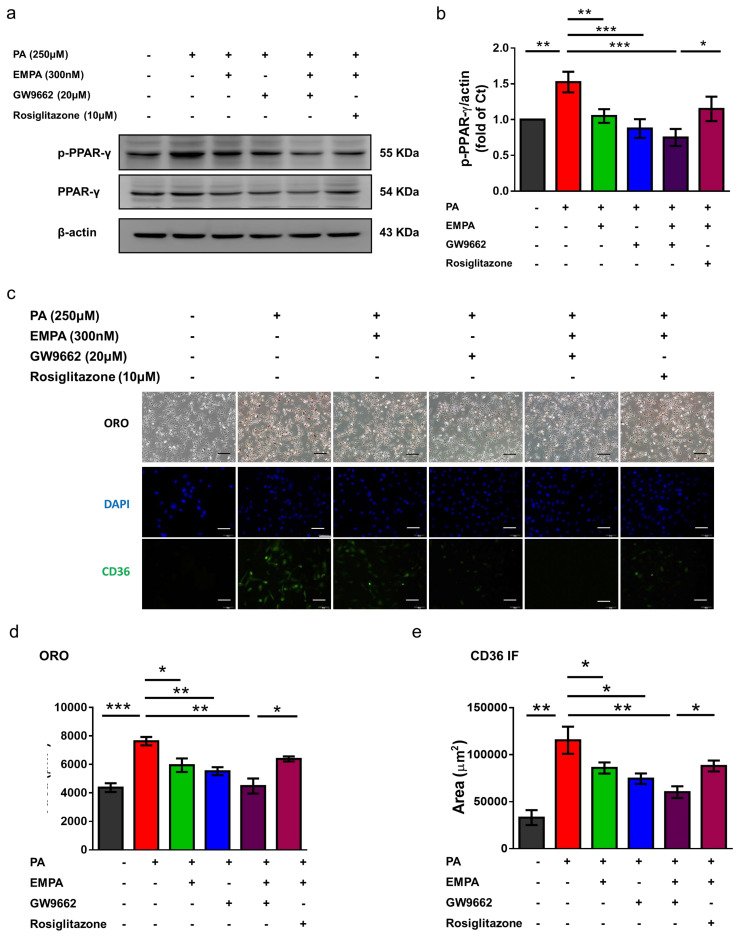
Figure 7.
Empagliflozin mediates CD36 expression and reduces lipid accumulation via PPAR-γ phosphorylation in HK-2 cells. HK-2 cells were cultured in a medium with 1% bovine serum albumin, PA (250 μM), empagliflozin (300 nM), GW9662 (20 μM), and rosiglitazone (10 μM). (a,b) Western blotting reveals that empagliflozin and GW9662 attenuate PA-induced PPAR-γ phosphorylation, and rosiglitazone can reverse this effect. (c,d) Based on representative Oil red O-stained images, GW9662 and empagliflozin attenuate PA-induced lipid droplet deposition, and rosiglitazone can aggravate this parameter (Scale bars 50 μm). (c,e) Based on the immunofluorescent assessment, GW9662 and empagliflozin attenuate PA-induced CD36 upregulation, and rosiglitazone can reverse this effect. The histograms represent mean ± standard error (SE) from 6 experiments. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. EMPA, empagliflozin; IF, immunofluorescence; ORO, Oil red O; PA, palmitic acid; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor.