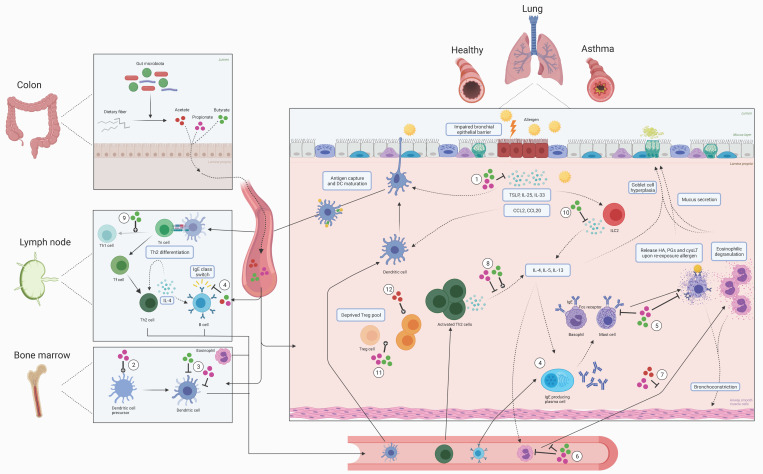
Figure 3.
Effects of SCFAs on the immune response in allergic asthma. Upon allergen exposure the airway epithelial barrier is damaged and activated, leading to type 2 driving mediator release and DC activation. These DC capture allergens and migrate to the mediastinal lymph nodes, where allergen presentation by DCs stimulates Th2 differentiation. Th2 cells instruct allergen-specific B cells to produce IgE (isotype switching). Th2 and plasma cells migrate to the mucosal tissue in the bronchi. Activated Th2, ILC2 and allergen-IgE stimulated mast cells induce eosinophil infiltration (eosinophilic airway inflammation) and asthma symptoms. Tregs in asthma patients are dysfunctional. (1) Propionate and butyrate increase tight junction protein expression and inhibit MAPK pathways, thereby restoring/inhibiting epithelial barrier dysfunction. (2) Propionate increases DC and macrophage precursor numbers (3) Propionate reduces DC activation and lowers MCHII expression, butyrate hampers DC maturation, lowers its migration efficacy and antigen capture efficiency. (4) Acetate, propionate, and butyrate reduce IgE isotype switching. (5) Propionate and butyrate hamper expression of FcεR-related genes, thereby reducing allergen/IgE triggered degranulation and asthma symptoms. (6) Propionate and/or butyrate may induce apoptosis in eosinophils, hinder migration from the bone marrow, and prevent adhesion of eosinophils to endothelial cells, hampering their infiltration into the lungs. (7) Acetate and propionate can also prevent airway infiltration by eosinophils. (8) Propionate decreases IL-13 release by Th2 cells, which may reduce goblet cell hyperplasia, mucus production, chronic inflammation, and allergen specific-IgE levels, while butyrate promotes cytokine production. (9) Butyrate induces expression of Th1 transcription factor T-bet and IFNγ. (10) Butyrate inhibits ILC2-mediated cytokine release. (11) Propionate and butyrate facilitate generation of extrathymic Tregs, and butyrate promotes Treg differentiation. (12) Acetate increases acetylation FOXP3 promotor. Full arrows with fading represent transition. Full arrows without fading represent migration. Dotted arrows with fading represent cytokine or chemokine induced stimulations. TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin; IL, interleukin; CCL, chemokine ligand; Th2, T helper cell type 2; Tf, follicular T cell; IgE, immunoglobulin E; ILC2, type 2 innate lymphoid cells; HA, histamine; PGs, prostaglandins; cysLT, cysteinyl leukotrienes; Fcε, fragment crystallizable region epsilon; Treg, regulatory T cell. The possible mechanisms of action shown in this cartoon are a compilation of SCFA effects derived from in vitro and/or in vivo studies.