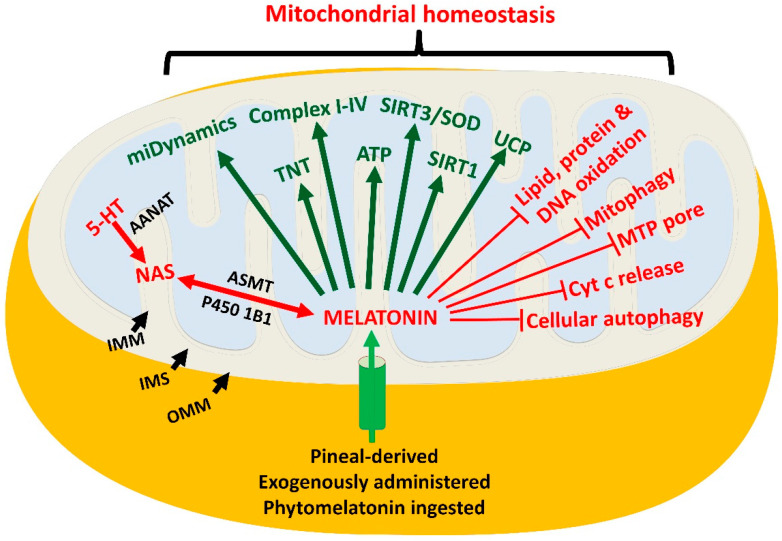
Figure 3.
Representative actions of melatonin that involve the mitochondria. Melatonin, derived from the pineal gland, after supplemental ingestion or consumed in the diet is taken up by cells and transported into the mitochondria via the oligopeptide transporters, PEPT1/2. All cells are believed to synthesize melatonin in their mitochondria via the conventional pathway as described in the pineal gland. In mitochondria, melatonin can be reverse-metabolized to its precursor, N-acetylserotonin (NAS); this involves the extrahepatic monooxygenase enzyme, P450 1B1. Thus, the changes induced by melatonin may also involve NAS production. The most recently discovered actions of melatonin that involve the mitochondria are its effects on tunneling nanotubes (TNT) which allow for the transfer of mitochondria between cells. 5-HT = serotonin; AANAT = arylalkyl-N-acetyltransferase; ASMT = acetyl serotonin methyltransferase; Cyt c = cytochrome c; IMM = inner mitochondrial membrane; IMS = Intermembrane space; miDynamics = mitochondrial dynamics; MTP = Mitochondrial permeability transition pore; OMM = outer mitochondrial membrane; UCP = uncoupling protein; SOD = superoxide dismutase.