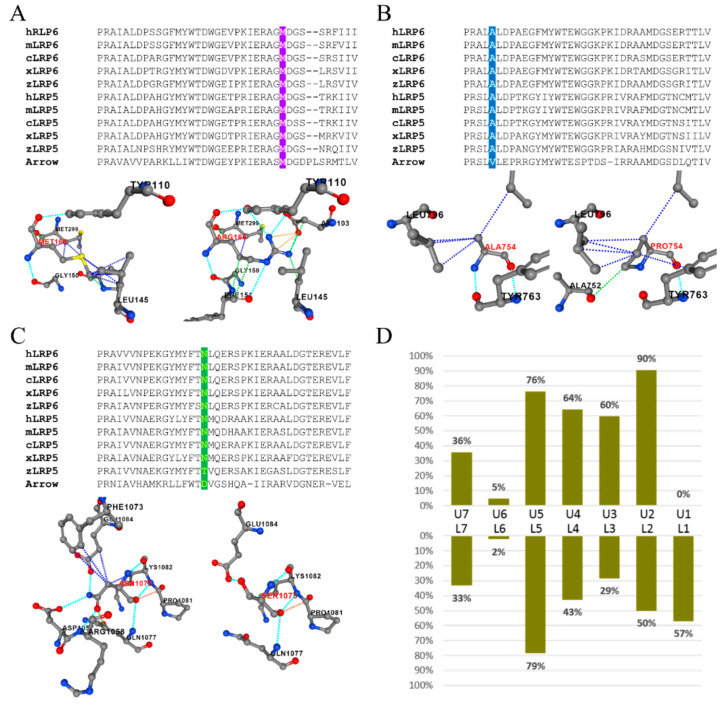
Figure 5.
Amino acid sequence alignment and structural prediction of LRP6 missense mutations. (A) Alignment of P1B3 domain (a.a. 140-177 of human LRP6). Methionine168 is extremely conserved throughout evolution. The p.(Met168Arg) mutation was predicted to be highly destabilizing. (B) Alignment of P3B3 domain (a.a. 750-787 of human LRP6). The Alanine754 is extremely conserved among orthologs of LRP6 and LRP5. The p.(Ala754Pro) mutation was predicted to be highly destabilizing. (C) Alignment of P4B3 domain (a.a. 1059-1097 of human LRP6). While Asparagine1075 is highly conserved among orthologs of LRP6 and LRP5, zebrafish LRP5 and Drosophila Arrow use threonine and aspartate, respectively, at this position. The p.(Asn1075Ser) mutation was predicted to destabilize local conformation. (D) Percentage of missing teeth in each tooth type of 21 patients with loss-of-function LRP6 mutations. The missing tooth numbers from the right and left sides were pooled together. Key: U, maxillary; L, mandibular; 1, central incisor; 2, lateral incisor; 3, canine (cuspid); 4, first premolar (bicuspid); 5, second premolar (bicuspid); 6, first molar; 7, second molar.