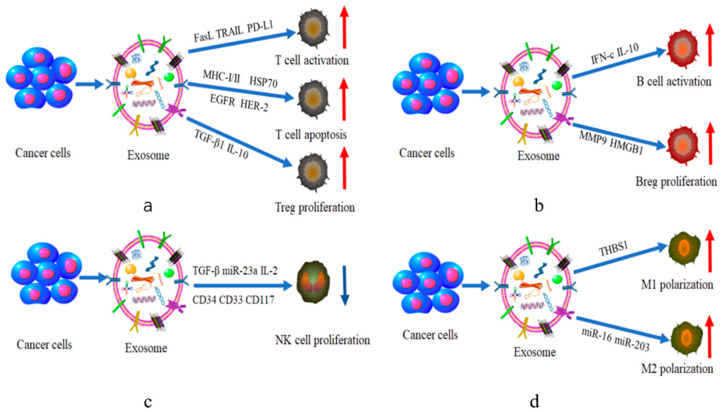
Figure 2.
The effect of tumor-derived exosomes on immune cells. (a–d) respectively show the regulatory effects of various signal molecules of tumor-derived exosomes on the proliferation and differentiation of T cells, B cells, NK cells and macrophages. (MHC-I(II), major histocompatibility complexes; HSP70, heat shock protein70; EGFR HER-2, growth factor receptors; FasL TRAIL PD-L1, tumor necrosis factor–related apoptosis-inducing ligand; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; IL-10, Interleukin-10TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; CD34 CD33 CD117, NK cells receptors; IFN-c, pro-inflammatory factors; IL-10, anti-inflammatory factors; MMP9, matrix metalloproteinase 9; HMGB1, an evolutionarily conserved DNA-binding nuclear protein; THBS 1, a protein with strong anti-inflammatory properties).