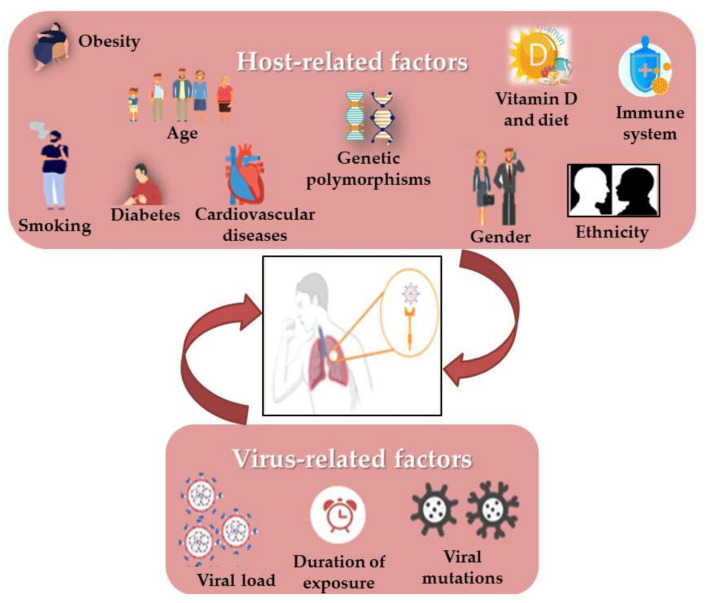
Figure 2.
Host and virus-related factors affecting COVID-19 outcome. Several factors related to the virus and to the host could account for COVID-19’s severity among individuals. A strong immune response is essential to eliminate the virus before its progression to more severe stages; therefore, harmful behaviors such as sedentary lifestyle, obesity, elevated tobacco consumption and unhealthy diet may weaken the immune system and render the host more sensitive to the virus. Health status is yet another factor influencing the clinical manifestations of SARS-CoV2 infections. As such, people of older age, especially those with comorbidities such as diabetes and lung and cardiovascular diseases may experience a more severe disease outcome. Moreover, the risk seems to be higher in males than in females, possibly because of the hormonal differences between the two genders as well as their genetic background, especially in the RAS components. RAS overactivity has also been described in metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes and obesity, all high-risk conditions for COVID-19 infection and severe disease. On the other hand, a higher viral load of SARS-CoV-2 as well as a sufficient duration of exposure to the virus could be related to more severe illness and even death. More importantly, the viral genetic mutations may favor the appearance of more severe variants, which could have a higher infectivity rate as well as a higher fatality rate among sensitive populations.