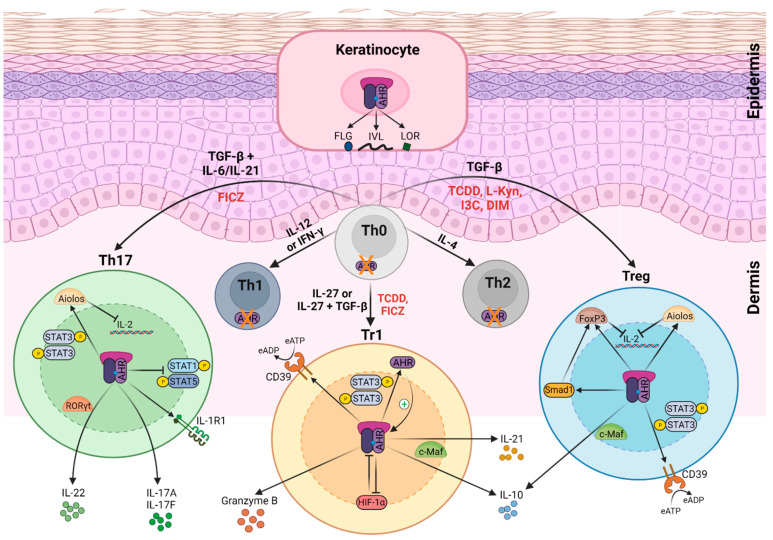
Figure 2.
Effects of AHR signaling in keratinocytes and different T cell subsets. AHR expression depends on T helper (Th) cell subsets. In naïve CD4+ T cells (Th0), Th1 cells, and Th2 cells, AHR expression is negligible. Th17 express the highest AHR levels and regulatory T (Treg) cells and T regulatory type 1 (Tr1) cells show intermediate levels. AHR’s activation exerts multiple effects on T cells. Engagement by particular ligands—such as 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), 6-formylindolo [3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ), L-kynurenine (L-Kyn), indole-3-carbinol (I3C), or 3,3′-diindolylmethane (DIM) (indicated in red)—activate transcriptional programs, which regulate the effector functions of AHR-expressing T cell subsets. In Th17 cells, the AHR enhances interleukin (IL)-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 release, in cooperation with RAR-related orphan receptor (ROR)γt. The AHR upregulates IL-1 receptor type 1 (IL-1R1) expression in Th17 cells. The AHR also inhibits signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)1 and STAT5, which negatively regulates the Th17 program, and together with STAT3, induced Aiolos expression that resulted in IL-2 silencing. In Tr1 cells, the AHR interacts with musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma (c-Maf) to induce the expression of IL-10 and IL-21, and with STAT3 to drive CD39 expression and its own expression, which acts as a positive feedback loop. The AHR also upregulates the expression of granzyme B and promotes hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α degradation. Similarly, the AHR induces IL-10 and CD39 in Treg cells, upregulates the expression of forkhead box (Fox)P3, and mothers against decapentaplegic homolog (Smad)1 and Aiolos. Smad1 controls the expression of FoxP3 and Aiolos cooperates with FoxP3 to repress IL-2 transcription. In keratinocytes, the AHR triggers the expression of genes of the epidermal differentiation complex (EDC) (described in the text) which encodes involucrin (IVL), loricrin (LOR), and filaggrin (FLG) proteins, among others. IFNγ—interferon gamma; TGF-β—transforming growth factor beta; CD39—cluster of differentiation 39; P—phosphorylation; eATP—extracellular adenosine triphosphate; eADP—extracellular adenosine diphosphate. Figure was created with BioRender.com.