Figure 1.
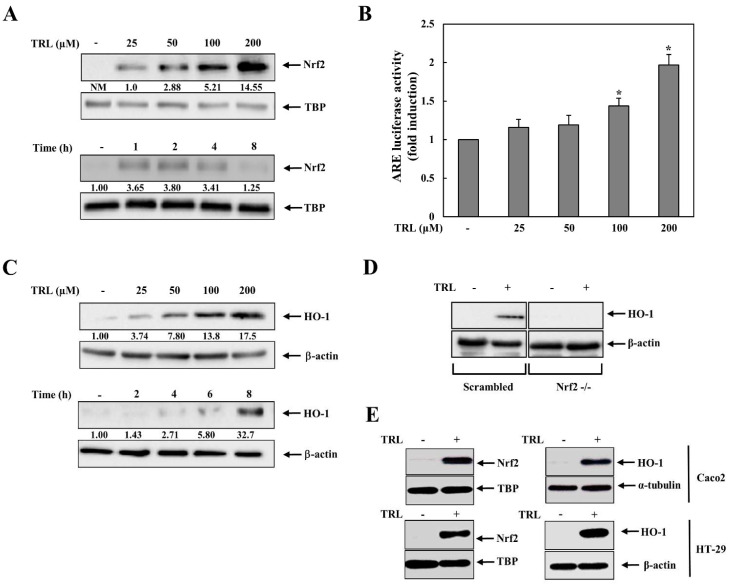
Tranilast (TRL) activates the Nrf2-HO-1 pathway. (A) Upper panel: HCT116 cells were treated with various concentrations of TRL for 2 h. The nuclear Nrf2 protein levels were assessed by western blotting. Lower panel: HCT116 cells were treated with TRL (200 μM) for the indicated times. The nuclear Nrf2 protein levels were assessed by western blotting. (B) Upper panel: HCT116 cells were treated with various concentrations of TRL for 8 h. The hemeoxygenase-1 (HO-1) protein levels were assessed by western blotting. Lower panel: HCT116 cells were treated with TRL (200 μM) for the indicated times. The HO-1 protein levels were assessed by western blotting. (C) HCT116 cells were cotransfected with an ARE-responsive luciferase reporter plasmid and a CMV Renilla luciferase plasmid for 24 h. The cells were treated with various concentrations of TRL for 8 h and ARE-responsive luciferase activity was measured and normalized to CMV Renilla luciferase activity. (D) Control (scrambled) and Nrf2-knockdown HCT116 cells (Nrf2-/-) were treated with TRL (200 μM) for 8 h. The HO-1 protein levels were assessed by western blotting. [E] Caco-2 cells and HT-29 cells were treated with TRL (200 μM). The nuclear Nrf2 and HO-1 protein levels were assessed after 2 and 8 h, respectively, by western blotting. For western blotting in (A,C,D,E), equivalent loading of proteins was verified using TATA box protein (TBP) for nuclear Nrf2 protein and β-actin for HO-1 protein. NM, not measurable. The data in (B) are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3) *: p < 0.05 vs. control.