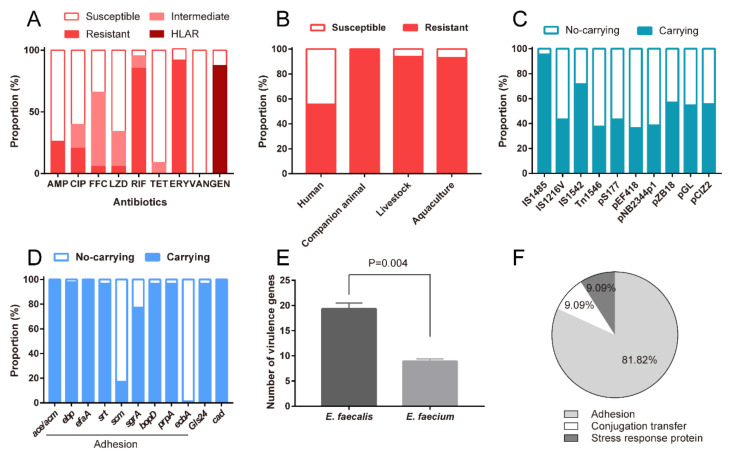
Figure 3.
Risks of probiotic enterococcal isolates. (A) Resistance rates of probiotic enterococcal isolates to different antimicrobial drugs. (B) Resistance rates of probiotic enterococcal isolates used for different application targets. (C) Carrying rates of different mobile genetic elements. (D) Carrying rates of different virulence genes. (E) The number of virulence genes in E. faecalis and E. faecium isolates. (F) Different functions of virulence genes in these probiotic enterococcal isolates. Differences in E were statistically analyzed by Student’s t-test. p ≤ 0.05 was considered to be significant.