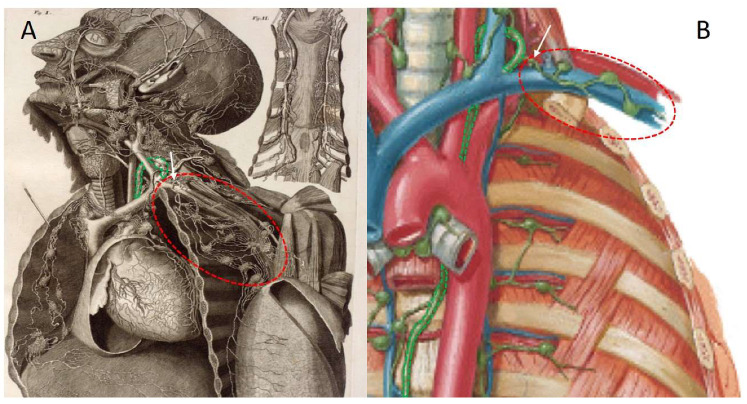
Figure 2.
Lymphatic anatomy of the upper quadrant, showing the thoracic duct and the subclavian lymphatic trunk connected to its network of lymph nodes. The thoracic duct is highlighted in green. The subclavian lymphatic trunk (with the main vessel indicated by a white arrow) and the connecting lymph nodes are circled in red. (A) This historical plate provides an unobstructed overview of the lymphatics in the area of interest. Note that the subclavian lymphatic trunk does not first connect to the thoracic duct before joining the venous angle. Adapted from the original atlas plate of Mascagni (1787) [13] (Library of Medicine and Pharmacy, University of Pisa). (B) In this modern plate, the subclavian lymphatic trunk is much more stylised and it connects directly to the thoracic duct. Adapted from Netter’s atlas of human anatomy [74].