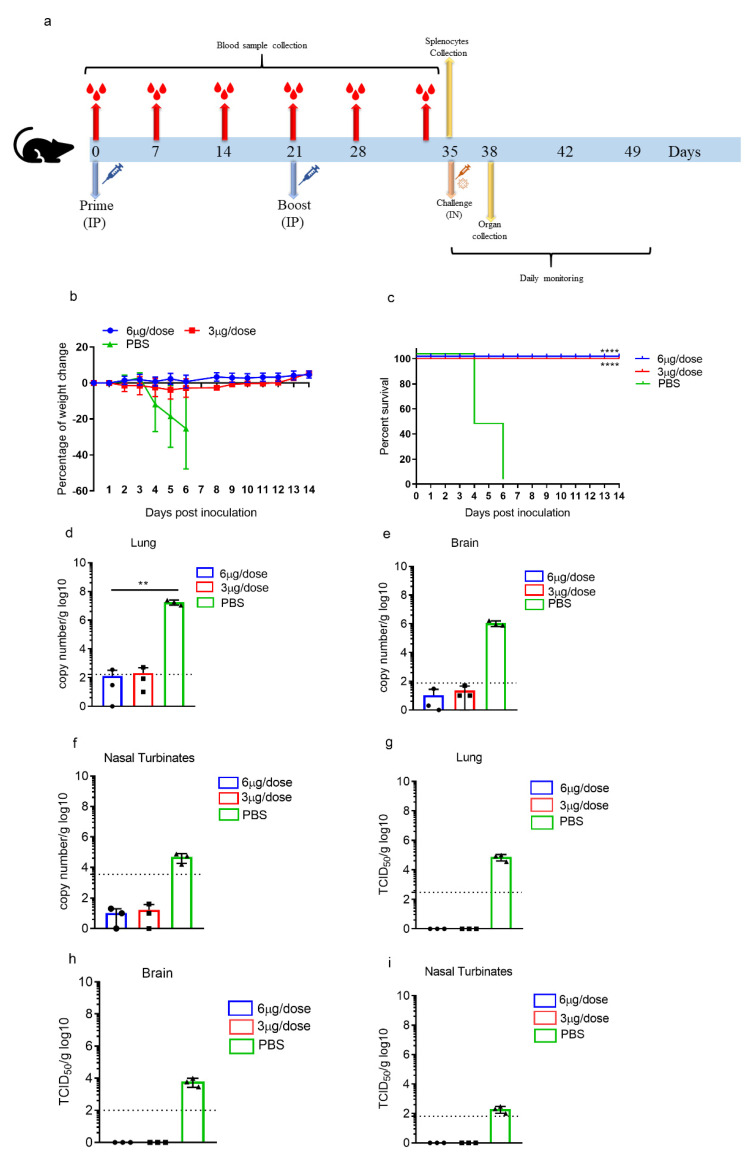
Figure 3.
Protective efficacy of ERUCoV-VAC in K18-hACE2 transgenic mice. (a) Scheme of sample collection, immunization regimens, and SARS CoV-2 challenge. Groups of K18-hACE2 transgenic mice immunized on days 0 and 21 with doses of 3 µg (n = 13) or 6 µg (n = 10) of ERUCoV-VAC or with a placebo (n = 13) via the intraperitoneal route. The K18-hACE2 mice (n = 10 per group) were challenged at 2 weeks after the second immunization with 5 × 104 TCID50 of SARS-CoV-2 in a volume of 60 µL by the intranasal route. Bodyweight (b) and survival (c) were evaluated according to the indicated timeline. The K18-hACE2 transgenic mice that lost ≥ 25% of their initial body weight were humanely euthanized. On day 3 after the challenge, three K18-hACE2 transgenic mice in each group were euthanized, and lungs, brains, and nasal turbinates were collected for qPCR and virus titration via TCID50 assay. qPCR was performed by targeting viral N gene for lungs (d), brains (e), and nasal turbinate (f) using a Diagnovital real-time PCR kit. A standard curve was generated using a viral RNA. Ten-fold dilutions of viral RNA were prepared, and negative control samples were included in each assay. The Ct value for each sample was converted into log10 viral copies/g tissue according to the standard curve. The dotted line indicates the highest value measured in the normal control group, which were 2.16 log10, 1.75 log10, and 3.35 log10 N copy number/g in the lungs, brains, and nasal turbinates, respectively. Live virus titres of the lungs (g), brains (h), and nasal turbinates (i) were determined via TCID50 assay at day 3 post-challenge. The statistical significance was assessed using a two-way ANOVA test, and p values less than 0.01 were considered to be statistically significant where ** denotes 0.01. Error bars represent mean ± standard deviation.