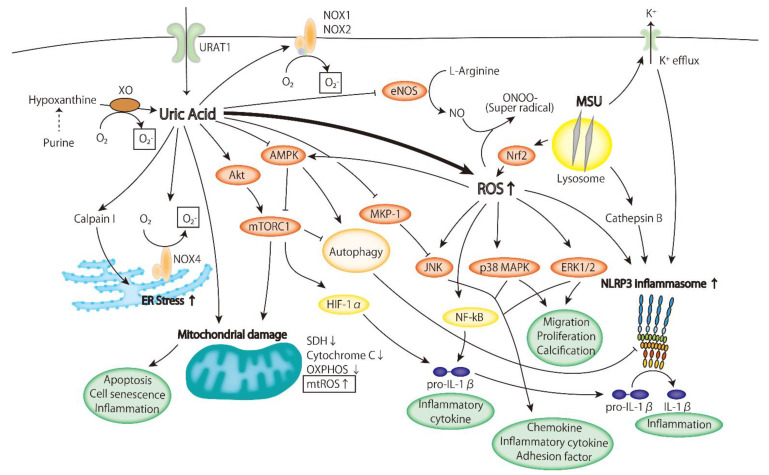
Figure 2.
The effect of uric acid on intracellular signaling pathways in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Intracellular uric acid induces reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and activates several inflammatory signaling pathways. XO, xanthine oxidase; NOX, NADPH oxidase; eNOS, endothelial NO synthase; MSU, monosodium urate; AMPK, AMP-activated kinase; Nrf2, Nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2; mTORC1, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; p38 MAPK, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; MKP-1, MAPK phosphatase-1; JNK, Jun N-terminal kinase; ERK, extracellular signaling-regulated kinase; HIF-1α, Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1α; SDH, succinate dehyderogenase; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; mtROS, mitochondrial ROS.