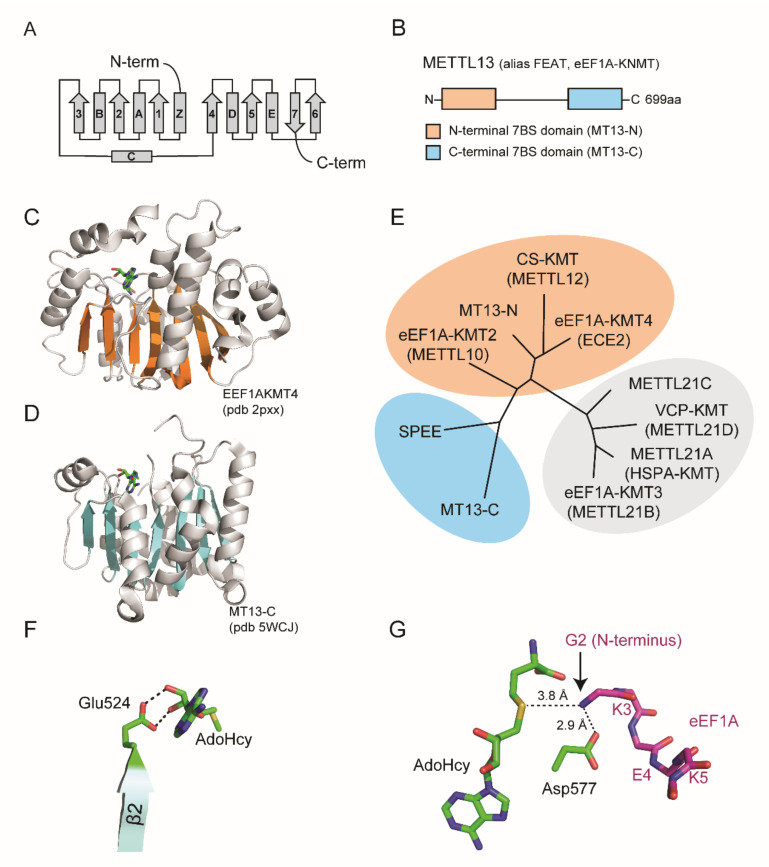
Figure 2.
Domain organization and structure of METTL13. (A) Topology diagram of seven beta strand (7BS) methyltransferase fold. (B) Domain architecture of METTL13. (C,D) Structure of MT13-N-like eEF1A-KMT4 protein and the MT13-C domain. Ribbon representations are shown with beta strands highlighted in orange for (C) eEF1A-KMT4 (pdb # 2PXX) and blue for (D) MT13-C (pdb # 5WCJ). (E) Phylogenetic tree of METT13 domains and related methyltransferase enzymes. The tree was generated using the “Phylogeny.fr” platform [22] using METTL21A–D as an outgroup. (F) Structural model of MT13-C interaction with AdoHcy. Potential hydrogen bonds between Glu524 and the ribose moiety of AdoHcy are indicated (dashed lines). (G) Structural model of MT13-C and eEF1A N-terminal substrate peptide. Possible hydrogen bonds between METTL13-Asp577 and the eEF1A substrate peptide (stick representation, purple) are shown. The relative position and distance of the eEF1A N-terminus in relation to AdoHcy is indicated. The model was generated using the glide dock approach [23].