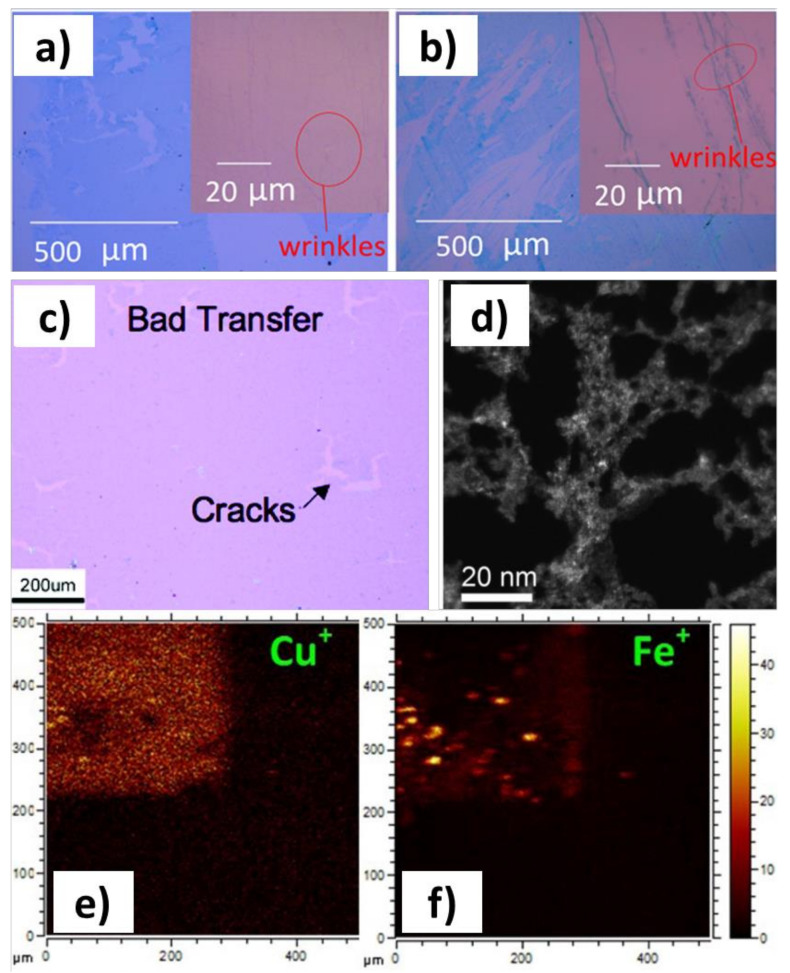
Figure 2.
Defects and impurities introduced during graphene transfer. (a) Optical micrograph of tears introduced from stamping transfer of graphene. (b) Tears and wrinkling introduced during the relamination step liquid-liquid interface transfer of graphene. (a,b) Adapted with permission from Ref. [26]. Copyright 2016 American Chemical Society. (c) Cracking of graphene introduced during polymer supported etching-based graphene transfer. (c) Adapted with permission from Ref. [27]. Copyright 2009 American Chemical Society. (d) Transmission electron micrograph (TEM) image of residual polymer contamination on graphene from a polymer supported etching transfer. (d) Adapted with permission from Ref. [28]. Copyright 2017 Cambridge University Press. (e,f) Time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS) maps of copper (e) and iron (f) ions showing residual metallic contamination from etching-based transfer. (e,f) Adapted with permission from Ref. [22]. Copyright 2015 American Chemical Society.