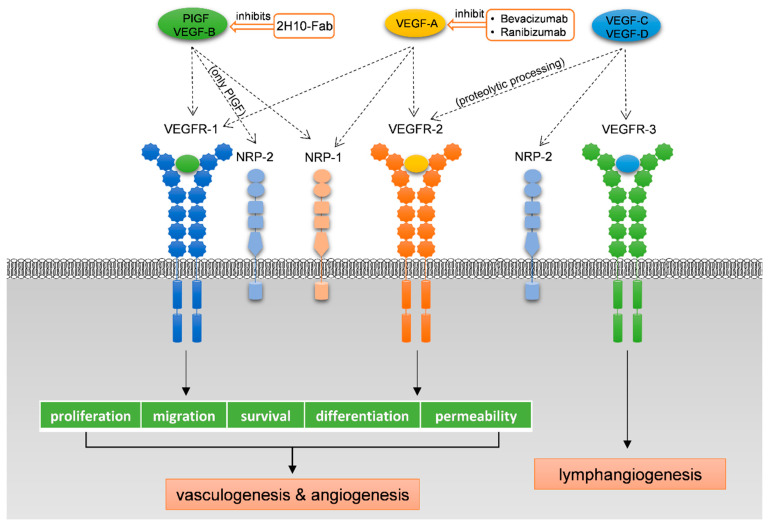
Figure 3.
VEGF signaling pathways and some representative antagonists. VEGF-A binds both VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2, whereas VEGF-B and PlGF only bind to VEGFR-1. VEGFR-1 modulates the action of VEGFR-2 and acts as a decoy or trap for VEGF-A. These pathways are relevant to vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. On the other hand, VEGF-C and VEGF-D bind to VEGFR-3, thereby regulating lymphangiogenesis and VEGFR-2 after proteolytic processing [36]. VEGF-A and VEGF-B can bind to co-receptor NRP-1, which promotes the activation of VEGFRs but is not essential [37,38]. PlGF isoforms (PlGF-2 and PlGF-4) can bind to both NRP-1 and NRP-2 as they have the insert of the heparin-binding domain [39]. NRP-2 binding of VEGF-C/D could lead to the formation of VEGF-C(D)/VEGFR-3/NRP-2 ternary signaling complexes, subsequently facilitating the physiological or pathological lymphangiogenesis [40].