Figure 2.
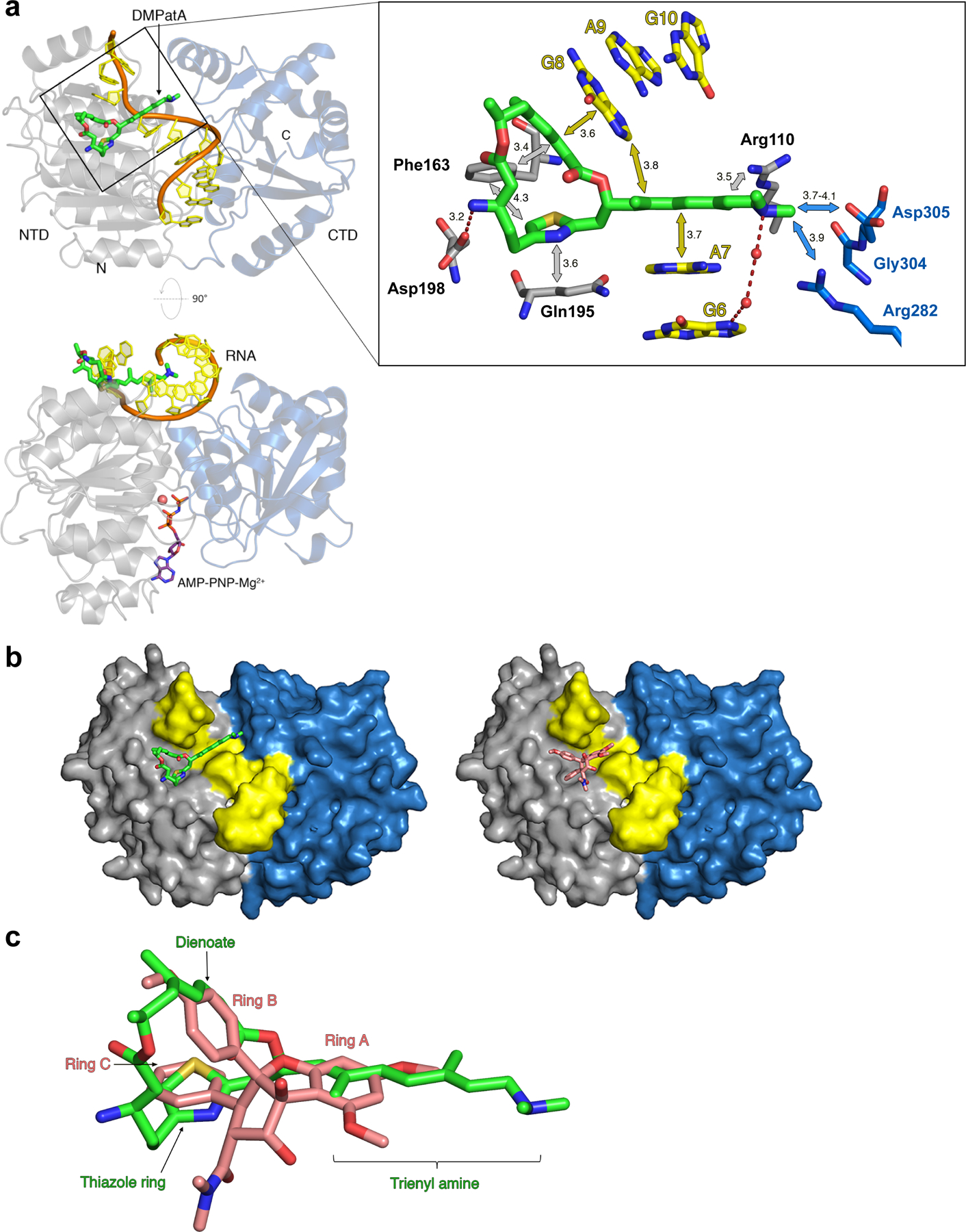
DMPatA interactions with eIF4A1 and poly (AG)5 RNA. a. Structure of DMPatA bound to eIF4A1•poly (AG)5•AMPPNP in two orthogonal views. NTD and CTD are represented as grey and blue ribbons, respectively. The RNA backbone is colored orange and the bases shown in yellow. DMPatA is shown in tube format with carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur colored green, blue, red and yellow, respectively. AMPPNP (omitted in the top view for clarity) is shown in tube format with pink carbon atoms and a magnesium ion shown as a pink sphere. A close-up of the boxed section in the top view reveals the main interactions between DMPatA and eIF4A1/RNA. NTD and CTD protein residues are shown in tube format with grey and blue carbon atoms, respectively. RNA is shown with yellow carbon atoms. Van der Waals/stacking interactions are indicated with grey/blue and yellow arrows for protein and RNA, respectively, along with corresponding distances in Angstroms. Dashed red lines refer to salt bridges with intervening water molecules represented as red spheres. The trienyl amine arm extends through the space created by the kink between RNA bases A7 and G8, linking the NTD (light grey) to the CTD (light blue). b. Comparison of the DMPatA (left; green) and RocA (right; pink) binding cavities in eIF4A. eIF4A1 is shown as a surface with the NTD, CTD and RNA colored grey, blue and yellow, respectively. c. Overlay of DMPatA (green) on RocA (pink) in the context of their binding to eIF4A1. Key components of each compound are labelled in green and pink for DMPatA and RocA, respectively. See also Figures S2 and S3.
