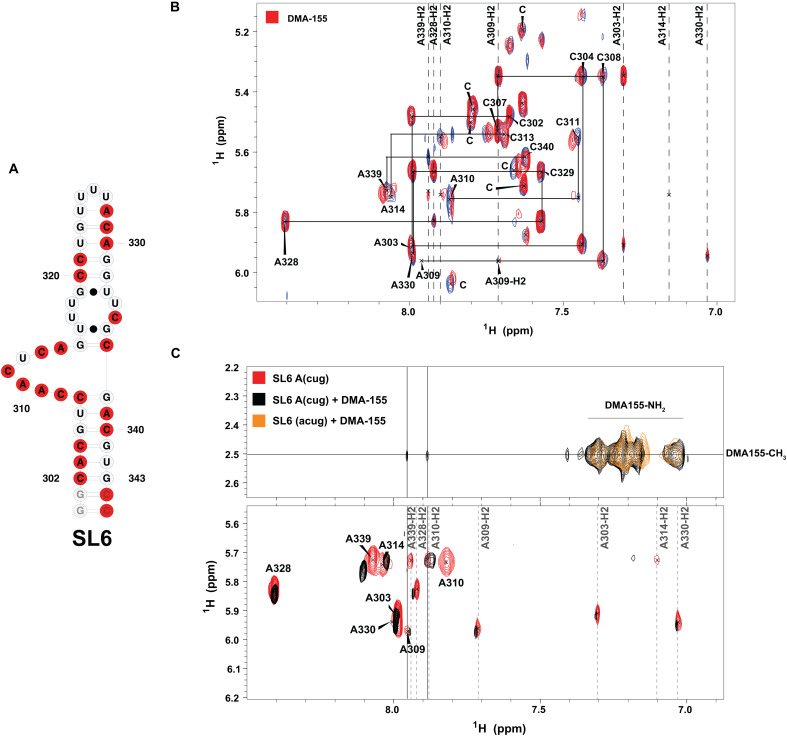
Fig. 8. Detailed interaction of DMA-155 with SL6.
(A) Representation of SL6 secondary structure and labeled nucleotides (red). (B) 1H-1H NOESY spectra (900 MHz, tm = 250 ms) of free UG(2H), AC(2H3′-5″) selectively labeled SL6 (blue) and its DMA-155 complex (red), which were collected in 25 mM K2HPO4 and 50 mM KCl (pH 6.2) at 308 K in 100% D2O, show that DMA-155 has a degree of binding specificity. (C) 1H-1H NOESY spectra (900 MHz and tm = 250 ms) of free CUG(2H), A(2H3’-5″) selectively labeled SL6 (red), its DMA-155 complex (black), and the fully deuterated RNA complexed with DMA-155 (orange) were collected in 25 mM K2HPO4 and 50 mM KCl (pH 6.2) at 308 K in 100% D2O. On the secondary structure of SL6, the nucleotides highlighted in red represent the labeling scheme of the RNA.