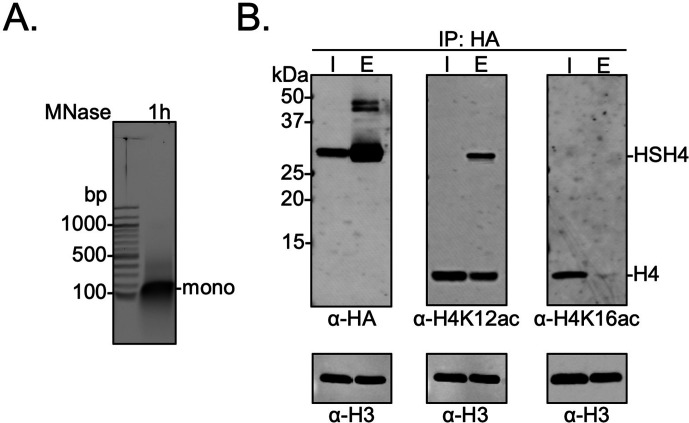
Figure 4. Biochemical crosstalk between H4 sumoylation and acetylation in HEK293T cells.
(A) Extended micrococcal nuclease digestion of chromatin to generate mononucleosomes that were detected by the presence of ~150 bp DNA in 1.5% agarose gels. (B) Immunoprecipitation (IP) from HEK293 cells transfected with HA-Su3(ΔGG)-H4 (HSH4). Input (I) and eluate (E) lanes correspond to undigested bulk chromatin and eluted HA-tagged mononucleosomes containing HSH4. Antibodies targeting H4K12ac and H4K16ac were employed to detect the degree of wild-type (wt) H4 and HSH4 acetylation in HA-tagged mononucleosomes. Total histone H3 in each sample was employed as an equal loading control.
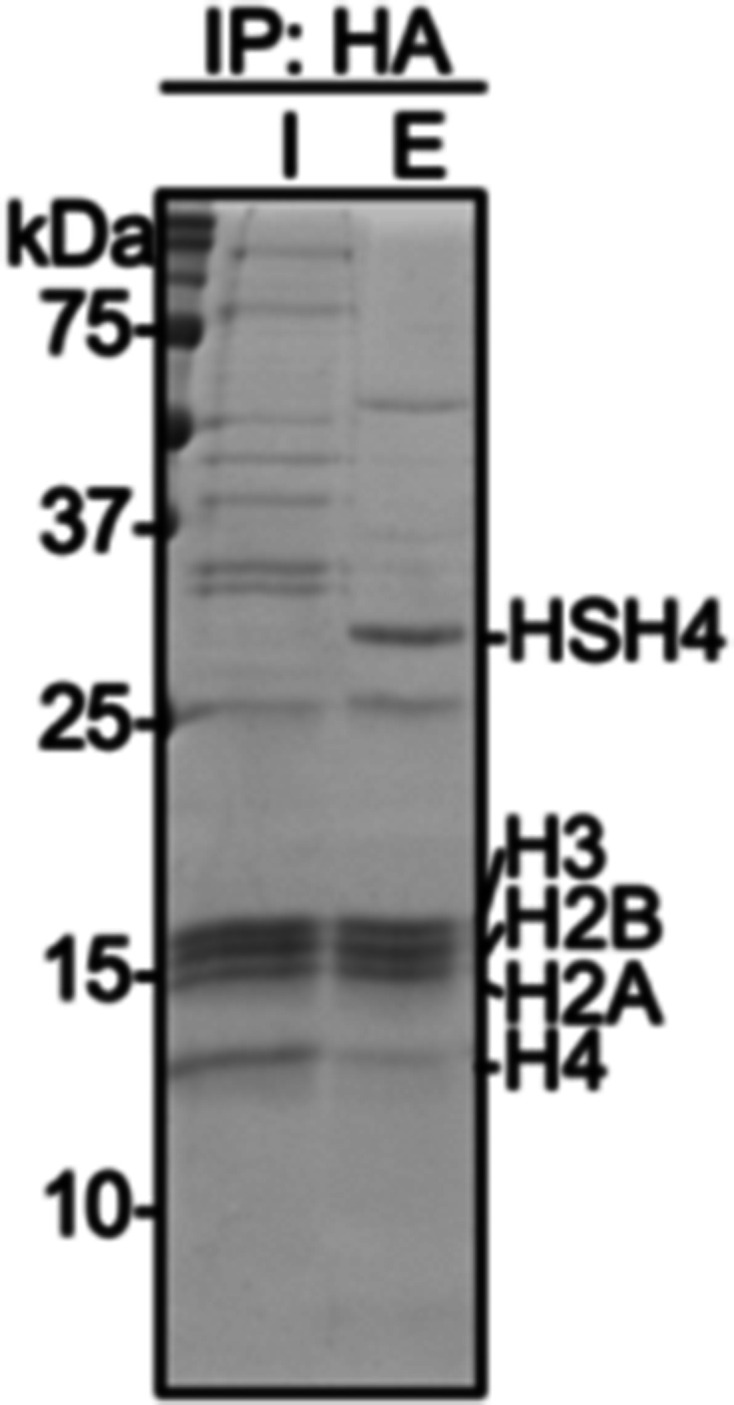
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel of input (I) and elution (E) samples from immunoprecipitation with anti-HA magnetic beads of micrococcal nuclease digested nuclear extracts prepared from HEK293T cells transfected with HA-Su3(ΔGG)-H4.