Extended Data Figure 9. The CCM effector KLF4 augments endothelial cell PI3K-mTORC1 signaling.
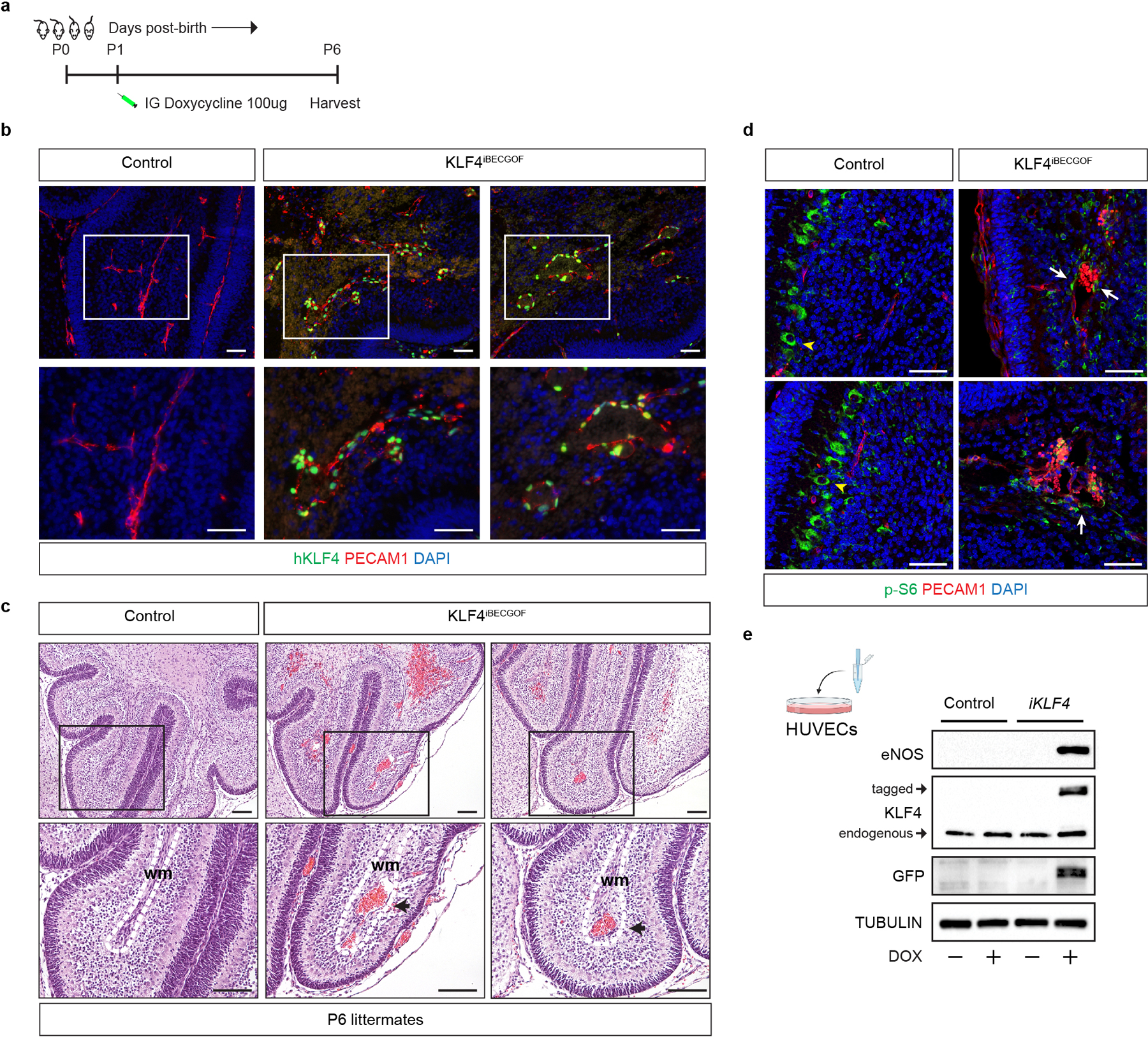
a, Schematic of neonatal endothelial induction of KLF4 expression in KLF4iBECGOF animals. b, Immunostaining for KLF4 and the endothelial cell marker PECAM1 in hindbrain sections from P6 control and KLF4iBECGOF animals is shown. Boxes in upper images denote area of magnified image immediately below. Immunofluorescence images representative of 6 tissue sections from n=4 individual animals/genotype. Scale bars, 50 microns. c, H-E stained sections of hindbrain from control and KLF4iBECGOF littermates. Boxes in upper images denote area of magnified image immediately below. Black arrows indicate lesions. Dotted lines outline the white matter of the cerebellum. wm, white matter. Note the dilated white matter venules similar to those observed with CCM loss of function and PIK3CA gain of function shown in Extended Data Figure 2. H-E histology representative of 6 tissue sections from n=4 animals/genotype. Scale bars, 0.1mm. d, Immunostaining for phospho-S6 ribosomal protein (p-S6) and the endothelial cell marker PECAM1 in hindbrain sections from P6 control and KLF4iBECGOF animals is shown. White arrows indicate p-S6 positive endothelial cells. Yellow arrowheads into non-endothelial p-S6 positive cells. Immunofluorescence images representative of 6 tissue sections from n=4 individual animals/genotype. Scale bars, 50 microns. e, Immunoblot detection of KLF4, KLF4-GFP, the KLF4 target gene eNOS in HUVECs without and with inducible lentiviral expression of KLF4-GFP (“iKLF4” cells) or control lentivirus. TUBULIN is shown as a loading control.
