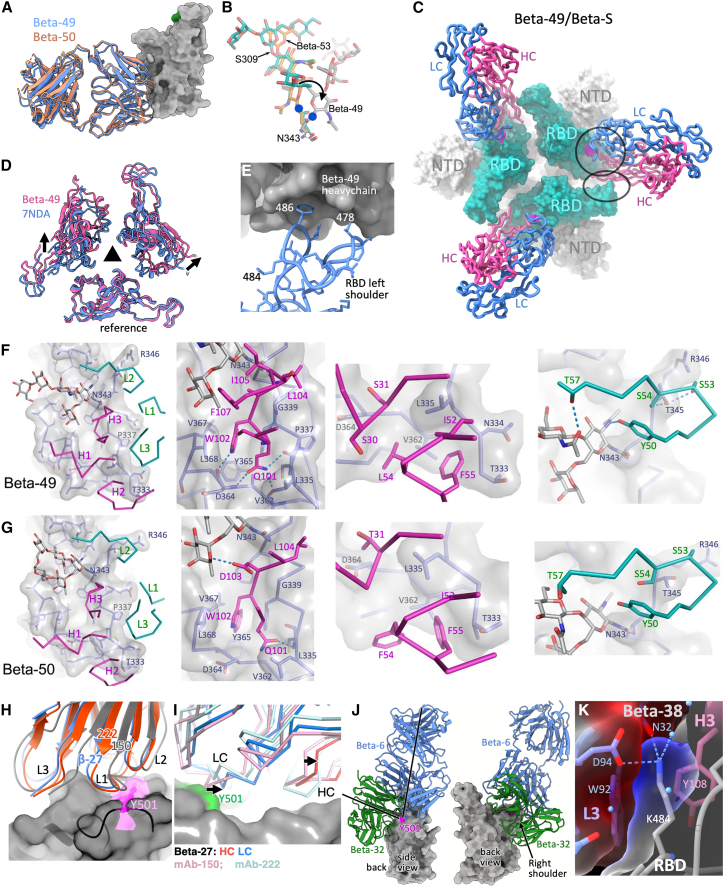
Figure 6.
Engagement of other Beta IgVH Fabs with the Beta RBD
(A) Almost identical binding of Beta-49 (blue) and Beta-50 (salmon) to the RBD.
(B) Overlay of N343 RBD glycan from the (green) (Pinto et al., 2020), Beta-53 (yellow) and Beta-49 (gray) complexes, the side chain rotated into an unfavorable conformation in the latter.
(C) Top view of the Beta-49 Fab/Beta S complex. S is shown as a surface (RBD cyan, position of glycan attachment to residue 343 magenta) while Beta-49 HC (dark pink) and LC (blue) are shown as cartoons. The HC contacts two RBDs, forming a primary (circle) and secondary (ellipse) epitope.
(D) Top view of the RBDs in all RBD down S (PDB 7NDA) and in the Beta-49 bound state. The 3-fold axis of S is shown. One RBD is superposed (reference), arrows show the movement in the other RBDs induced on binding Beta-49.
(E) Close up of the secondary epitope with some RBD residues marked.
(F) Close up of Beta-49/Beta S interaction. The RBD is shown as sticks and a surface (glycan at N343 as sticks only), and Fab as sticks colored by chain.
(G) Similar to (F) but for Beta-50.
(H and I) Comparison of the binding of Beta-27 with mAbs 150 and 222. (H) Residue 501 is highlighted on the RBD surface. (I) Side view of the right shoulder and neck of the RBD. Arrows show shifts due to repositioning the HC CDR3.
(J) Comparison of the attachment of Beta-6 and -32 to the RBD with axes (left panel) showing difference in pose.
(K) K484 is enclosed by the Beta-38 HC and LC CDR3s. See also Figure S4 and Tables S2 and S4.