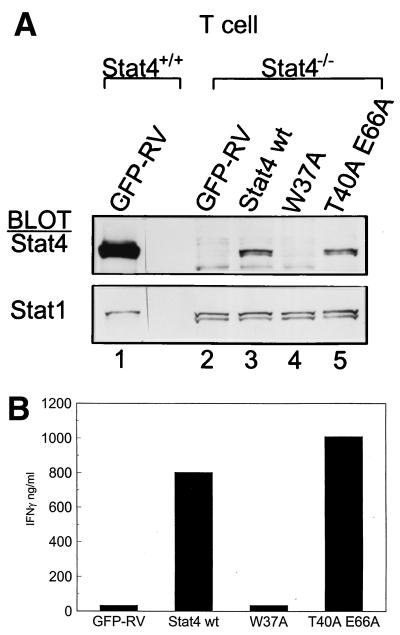
FIG. 6.
Loss of IL-12-induced Stat4 nuclear translocation and Stat4-dependent IFN-γ production from mutations in the Stat4 N domain. (A) DO11.10 TCR transgenic T cells from wild-type (Stat4+/+) or Stat4-deficient (Stat4−/−) mice were activated as described previously (29) and infected with empty GFP-RV retrovirus (GFP-RV) or retrovirus expressing wild-type Stat4 (Stat4 wt) or W37A or T40A E66A N domain mutations as indicated. Cells were grown in the presence of 10 U of IL-12 per ml and expanded for 7 days, and the infected T cells were purified by positive cell sorting for expression of GFP and murine CD4. Purified T cells were expanded by restimulation with irradiated BALB/c splenocytes and ovalbumin and treated with IL-12, nuclear extracts were prepared, and direct Western analysis was done for Stat4 and Stat1. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments. (B) T cells derived and purified as for panel A were analyzed for the production of IFN-γ in response to IL-12–IL-18 combined treatment. T cells were placed at 106 cells per well of a 48-well plate in 1 ml of medium and treated with IL-12 (10 U/ml) and IL-18 (100 U/ml) for 48 h, supernatants were harvested, and IFN-γ was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.