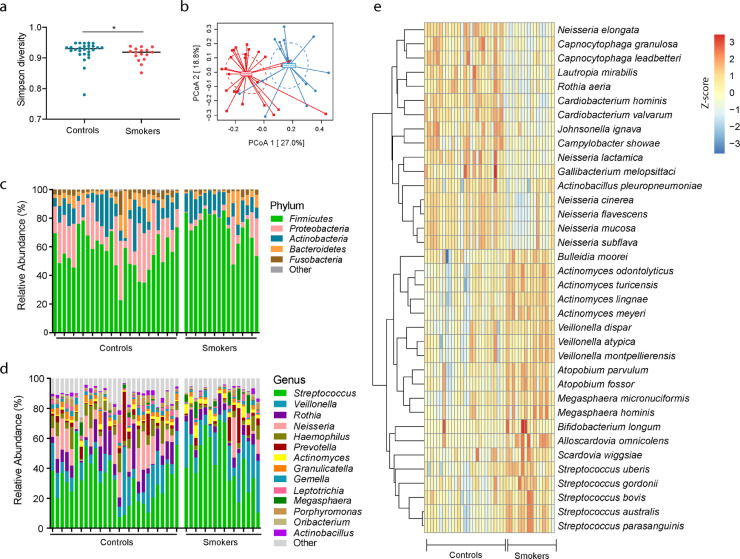
Fig. 1.
Oral microbiome in cannabis smokers (smokers) and non-smoking controls (controls). (a) The Gini Simpson diversity index (α-diversity) was used to compare the diversity of the oral microbial community between cannabis smokers and controls. (b) PCoA was conducted based on the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity distance to determine the beta diversity in cannabis smokers and controls. The statistical significance of the beta diversity was tested using the Multivariate Welch t-test. (c) The average relative abundance of each bacteria at the phylum level. (d) The average relative abundance of each bacteria at the genus level. (e) The species-level of the significantly different oral microbiome in cannabis smokers compared to controls after adjusting for FDR (p < 0.05), which included 16 species decreased and 20 species increased in cannabis smokers compared to controls.