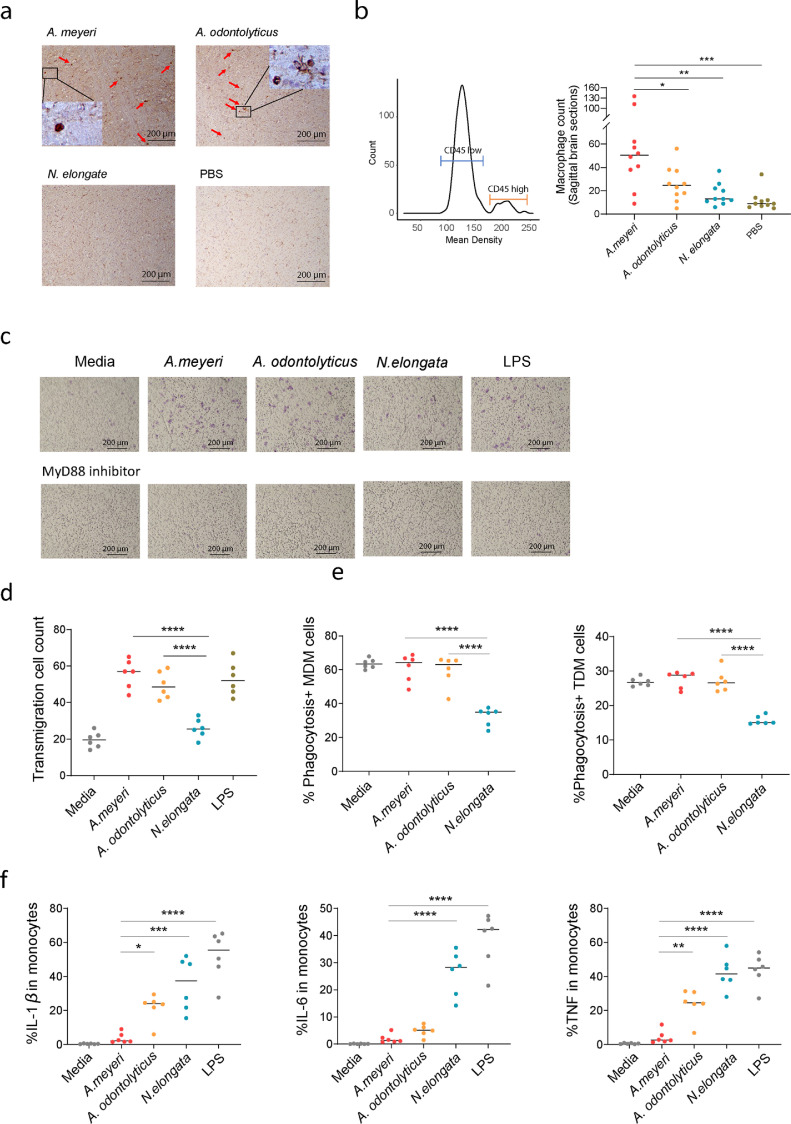
Fig. 4.
A. meyeri induced macrophage migration and/or infiltration to the brain in vivo and in vitro. (a) Macrophage infiltration was assessed in sagittal brain sections of mice by CD45 and macrophage morphology using IHC staining. Macrophages were labeled using red arrows. (b) The mean density and median levels of macrophage infiltration in the sagittal section of mouse brain using CD45 staining and macrophage morphology. (c) A. meyeri and A. odontolyticus, but not N. elongata induced THP-1 cell transmigration in the transwell assay which was prevented by MyD88 inhibitor. (d) Transmigrated THP-1 cell counts after treatment with A. meyeri, A. odontolyticus, N. elongata, LPS (E. coli 055:B5), or medium control. (e) The percentages of phagocytosis in THP-1 derived macrophage (TDM) and human monocyte-derived macrophage (MDM) in each condition. (f) The percentages of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α producing monocytes were evaluated using flow cytometry after stimulation with 1 × 107 units/ml of each bacteria or 2 ng/ml of LPS for 6 h. (One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test, *p < 0.05, ⁎⁎p < 0.01, ⁎⁎⁎p < 0.001, ⁎⁎⁎⁎p < 0.0001.)