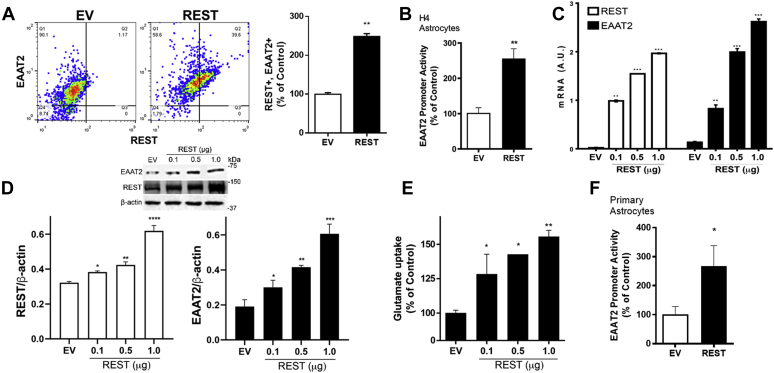
Figure 1.
REST positively regulates EAAT2 expression at the transcriptional level.A, after REST (1 μg) or empty vector (EV) transfection, H4 astrocytes were immunostained with anti-EAAT2 and anti-REST antibodies, followed by flow cytometry as described in the Experimental procedures section with quantification. B, astrocytes were cotransfected with the EAAT2 promoter and REST expression vectors, followed by luciferase assay as described in the Experimental procedures section. C and D, after REST transfection, astrocytes were prepared to measure levels of mRNA and protein of EAAT2 and REST, followed by quantitative PCR (C) and Western blotting (D), respectively. E, after REST transfection, glutamate uptake was assessed by measuring intracellular glutamate levels. F, the effects of REST on EAAT2 promoter activity were determined in primary mouse astrocytes. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 compared with the controls (Student's t test or one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test; n = 3 of biological replicates). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments. EAAT2, excitatory amino acid transporter 20; REST, repressor element 1-silencing transcription factor.