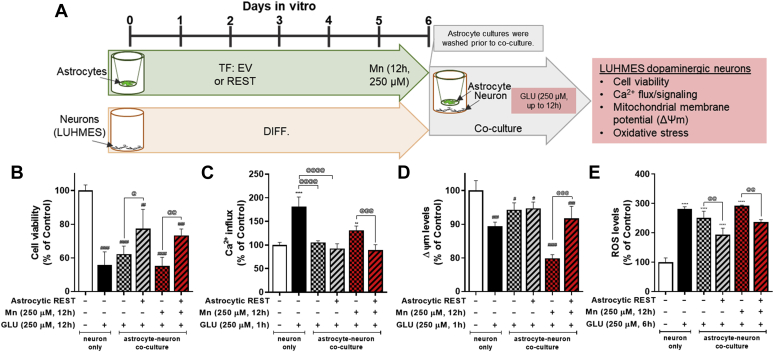
Figure 10.
Astrocytic REST attenuated Mn-induced excitotoxic neuronal injury in an astrocyte-LUHMES cell coculture.A, schematic representation of the experimental paradigm for H4 astrocyte-LUHMES coculture. B–E, effect of astrocytic REST in Mn-induced excitotoxic neuronal injury. REST-overexpressing astrocytes were exposed to Mn separately in transwells, followed by transferring transwells containing astrocytes into culture plates containing dopaminergic neuronal cells to create coculture conditions in the presence of glutamate (250 μM, 12 h). Neuronal toxicity was assessed for cell viability (B), Ca2+ influx (C), Δψm (D), and ROS production (E). ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; ##p < 0.01; ###p < 0.001; ####p < 0.0001, compared with the controls; @p < 0.05; @@p < 0.01; @@@p < 0.001; @@@@p < 0.0001 compared with each other (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test; n = 6). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments. LUHMES, Lund human mesencephalic; Mn, manganese; REST, repressor element 1-silencing transcription factor; ROS, reactive oxygen species.