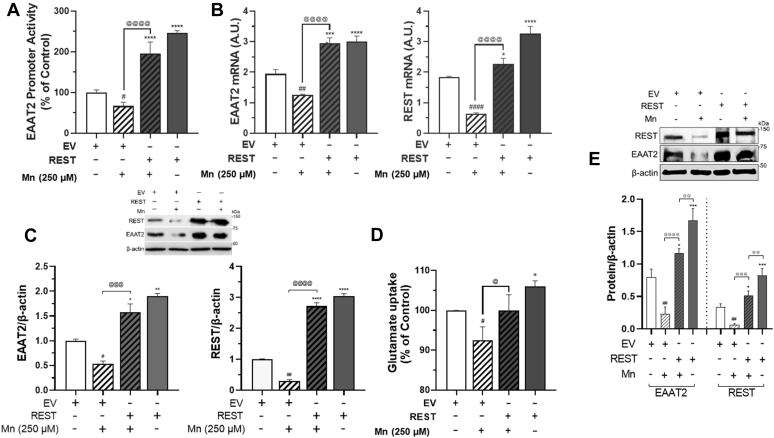
Figure 7.
REST attenuates Mn-repressed EAAT2 expression in astrocytes.A–C, after cotransfected with EAAT2 promoter and/or REST expression vectors, H4 astrocytes were exposed to Mn for 12 h to determine promoter activity, mRNA, and protein levels of EAAT2 and REST by luciferase assay (A), quantitative PCR (B), and Western blotting (C), respectively. D, REST-transfected astrocytes were exposed to Mn (250 μM) for 12 h, followed by intracellular glutamate assay for glutamate uptake as described in the Experimental procedures section. E, after REST was overexpressed in human primary astrocytes, cells were exposed to Mn (250 μM) for 12 h, followed by assessment of protein levels of REST and EAAT2 by Western blotting. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; #p < 0.05; ##p < 0.01; ####p < 0.0001, compared with the controls; @p < 0.05; @@@p < 0.001; @@@@p < 0.0001 compared with each other (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test; n = 3). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments. EAAT2, excitatory amino acid transporter 2; Mn, manganese; REST, repressor element 1-silencing transcription factor.