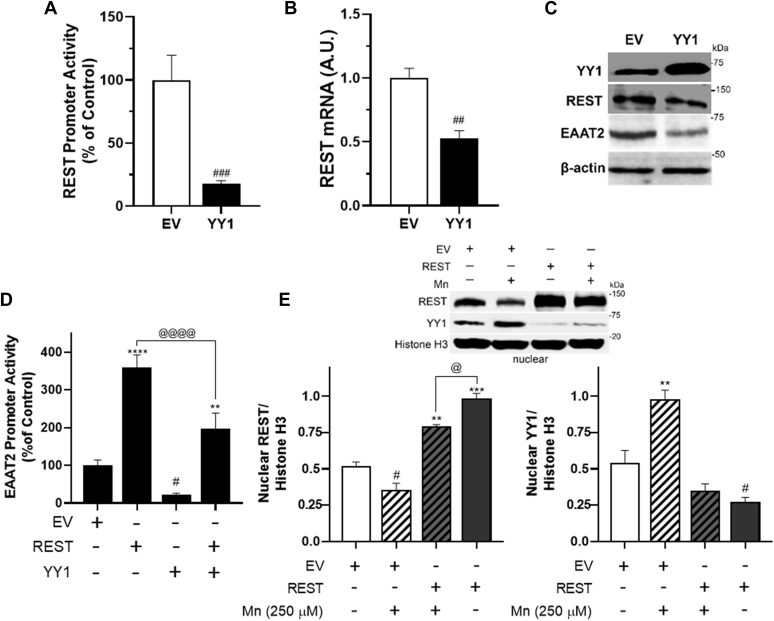
Figure 8.
YY1 represses REST, and REST overexpression abolished Mn-increased YY1 in astrocytes.A–C, H4 astrocytes were cotransfected with REST promoter and/or YY1 expression vectors, followed by assessing promoter activity, mRNA, and protein levels of REST, YY1, and/or EAAT2. D, after H4 astrocytes were cotransfected with EAAT2 promoter, REST, and/or YY1 vectors, EAAT2 promoter activity was measured. E, after REST-overexpressing H4 astrocytes were exposed to Mn, followed by nuclear fractionation, and Western blotting to determine nuclear REST and YY1 levels in H4 astrocytes. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; #p < 0.05; ##p < 0.01; ###p < 0.001 compared with the controls; @p < 0.05; @@@@p < 0.0001, compared with each other (Student's t test or one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test; n = 3). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments. EAAT2, excitatory amino acid transporter 2; Mn, manganese; REST, repressor element 1-silencing transcription factor; YY1, Yin Yang 1.