FIGURE 1.
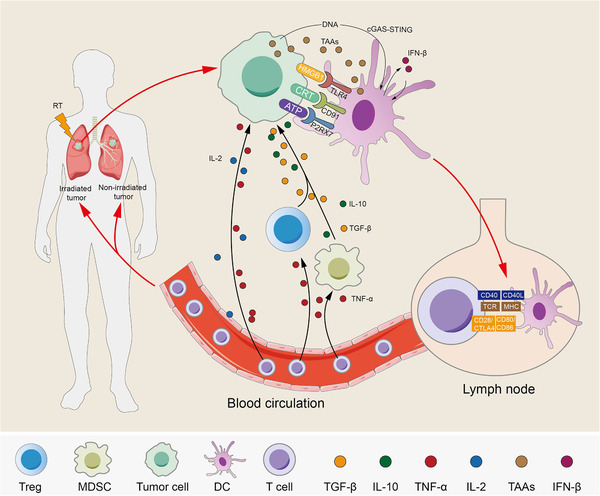
Radiotherapy‐induced effects on tumor cells. Radiotherapy (RT) induces immunogenic death of tumor cells which increases the release of tumor‐associated antigens (TAAs) and damage‐associated molecular patterns such as high‐mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and enhances the surface expression of calreticulin (CRT). Secretion promotes the activation and maturation of dendritic cells (DCs) through their corresponding receptors. DCs that sense cancer cell‐derived DNA induce interferon‐β (IFN‐β) production through the cyclic GMP‐AMP synthase (cGAS)‐ stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway. In turn, IFN‐β promotes the activation and maturation of DCs. DCs take up tumor‐associated antigens (TAAs) and migrate to draining lymph nodes and then present the TAAs on major histocompatibility complex class I (MHCI) to T cells through the T‐cell receptor (TCR), which requires the costimulatory molecules CD80/86‐CD28/cytotoxic T lymphocyte‐associated protein 4 (CTLA4) and CD40L‐CD40. Otherwise, these are not sufficient to cause T cell activation and proliferation in the absence of costimulatory signals. Activated T cells are transported to irradiated lesions and distant nonirradiated lesions through the blood circulation. At the same time, tumor cell immunogenic death leads to the release of cytokines, the immune‐promoting factors tumor necrosis factor‐α (TNF‐α) and interleukin‐2 (IL‐2) recruit activated T cells to kill tumor cells through upregulated MHCI, and the immunosuppressive factors such as TGF‐β and IL‐10 recruit immunosuppressive cells such as regulatory T cells (Tregs) and myeloid‐derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) to inhibit immune effects. However, activated T cells cause the apoptosis of Tregs and MDSCs through cytokines such as TNF‐α. Abbreviations: Radiotherapy, RT; tumor‐associated antigens, TAAs; high‐mobility group box 1, HMGB1; adenosine triphosphate, ATP; calreticulin, CRT; dendritic cells, DCs; interferon‐β, IFN‐β; cyclic GMP‐AMP synthase, cGAS; stimulator of interferon genes, STING; tumor‐associated antigens, TAAs; major histocompatibility complex class I, MHC1; T‐cell receptor, TCR; Cytotoxic T lymphocyte‐associated protein 4, CTLA4; tumor necrosis factor‐α, TNF‐α; interleukin‐2, IL‐2; Myeloid‐derived suppressor cells, MDSCs; P2X7 receptor, P2RX7; transforming growth factor‐β, TGF‐β; regulatory T cells, Tregs
