FIGURE 2.
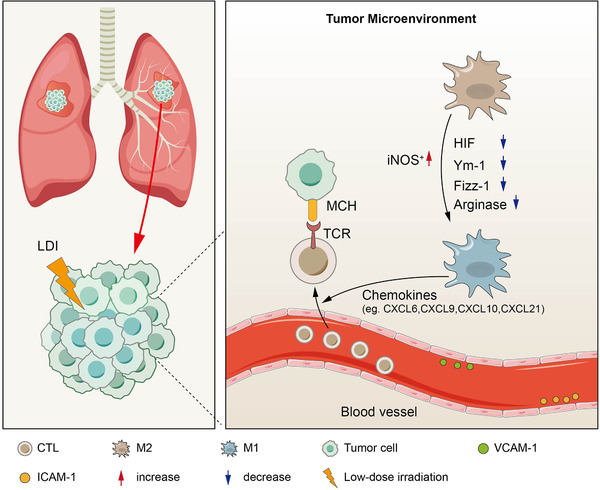
Low‐dose irradiation remodels the tumor microenvironment. Two main mechanisms exist by which radiation enhances tumor‐infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). One is increased expression of chemokines that enhance immune cell migration and invasion, and the other relates to changes in the vascular endothelium that enhance immune cell extravasation. Low‐dose irradiation (LDI) induces M1 macrophage polarization by regulating the corresponding molecules, such as inducible nitric oxide synthase‐positive (iNOS+), Hypoxia‐inducible factor‐1 (HIF‐1), chitinase‐like‐3 (Ym‐1), Found in the inflammatory zone‐1 (Fizz‐1), Arginase, and iNOS+ M1 macrophages, which produce chemokines to recruit effector T cells and cause T cell infiltration. LDI increases vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM‐1) and intercellular adhesion molecule‐1 (ICAM‐1) expression in human vascular endothelial cells, causing normalization of tumor vessels. Abbreviations: low‐dose irradiation, LDI; tumor‐infiltrating lymphocytes, TILs; inducible nitric oxide synthase‐positive, iNOS+; Hypoxia‐inducible factor‐1, HIF‐1; chitinase‐like‐3, Ym‐1; found in inflammatory zone‐1, Fizz‐1; M1 macrophages, M1; M2 macrophages, M2; vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, VCAM‐1; intercellular adhesion molecule‐1, ICAM‐1; major histocompatibility complex, MHC; T‐cell receptor, TCR; cytotoxic T‐lymphocyte, CTL; C‐X‐C motif chemokine, CXCL
