FIGURE 2.
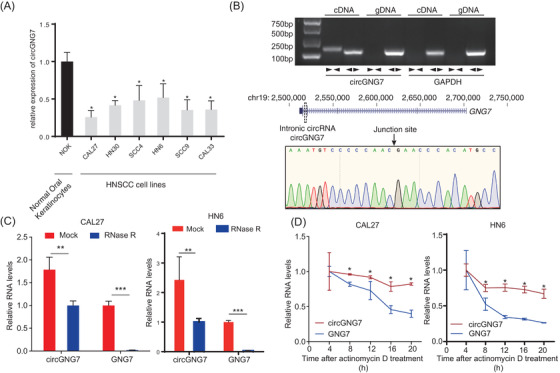
Evidence of circGNG7 as a circular RNA and its subcellular localization. (A) circGNG7 expression was measured in HNSCC cell lines and normal oral keratinocytes. (B) Schematic illustration of the origin and structure of circGNG7. The circular form of circGNG7 in cDNA and gDNA was validated by using divergent primers ( ) and convergent primers (
) and convergent primers ( ) in CAL27 cells. GAPDH was used as a linear RNA control. The head‐to‐tail splicing of circGNG7 was confirmed by Sanger sequencing in CAL27 cells. (C) RNA samples were treated with RNase R to remove linear RNAs, and circGNG7 was evaluated after RNase R digestion in CAL27 and HN6 cells. For qPCR normalization, the abundance of GNG7 was calculated by standardizing over the spike DNA control and setting the PBS control. (D) RT‐PCR for the abundance of circGNG7 and GNG7 in CAL27 and HN6 cells treated with actinomycin D at the indicated time points. Data are presented as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Abbreviations: HNSCC: head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; qPCR: quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction; RT‐PCR: reverse transcription PCR; GNG7: G protein subunit gamma 7; cDNA: complementary DNA; gDNA: genomic DNA
) in CAL27 cells. GAPDH was used as a linear RNA control. The head‐to‐tail splicing of circGNG7 was confirmed by Sanger sequencing in CAL27 cells. (C) RNA samples were treated with RNase R to remove linear RNAs, and circGNG7 was evaluated after RNase R digestion in CAL27 and HN6 cells. For qPCR normalization, the abundance of GNG7 was calculated by standardizing over the spike DNA control and setting the PBS control. (D) RT‐PCR for the abundance of circGNG7 and GNG7 in CAL27 and HN6 cells treated with actinomycin D at the indicated time points. Data are presented as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Abbreviations: HNSCC: head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; qPCR: quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction; RT‐PCR: reverse transcription PCR; GNG7: G protein subunit gamma 7; cDNA: complementary DNA; gDNA: genomic DNA
