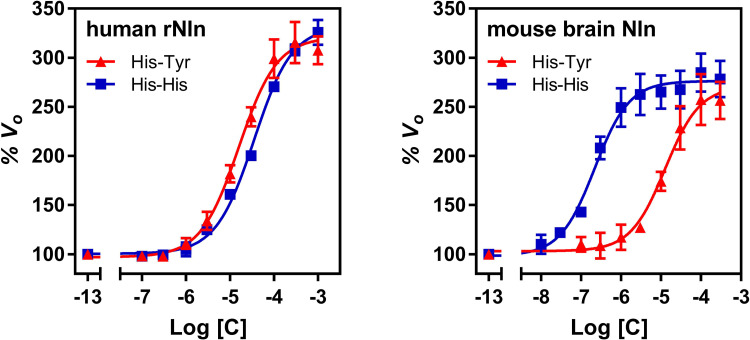
Fig. 3.
The effect of His-Tyr and His-His on catalytic activity of recombinant human (left) and mouse brain–isolated (right) Nln. The panels document concentration-dependent effect of both compounds on hydrolysis of synthetic substrate at 15 µM (mean ± S.D., n = 4 independent experiments with duplicate samples for each condition). Note that the initial velocity of the hydrolysis in the absence of either compound corresponds to 100% on the vertical axis and −13 on the horizontal axis. With recombinant human Nln, A50 = 15.9 µM (95% CI, 13.0–19.3 µM) and Amax = 321% (95% CI, 313–330) for His-Tyr. For His-His, A50 = 35.1 µM (95% CI, 30.1–39.9 µM) and Amax = 332% (95% CI, 326%–338%). With mouse brain–isolated Nln, A50 = 12.7 µM (95% CI, 8.9–17.9 µM) and Amax = 271% (95% CI, 258%–285%) for His-Tyr. For His-His, A50 = 0.22 µM (95% CI, 0.16–0.29 µM) and Amax = 276% (95% CI, 269%–283%).