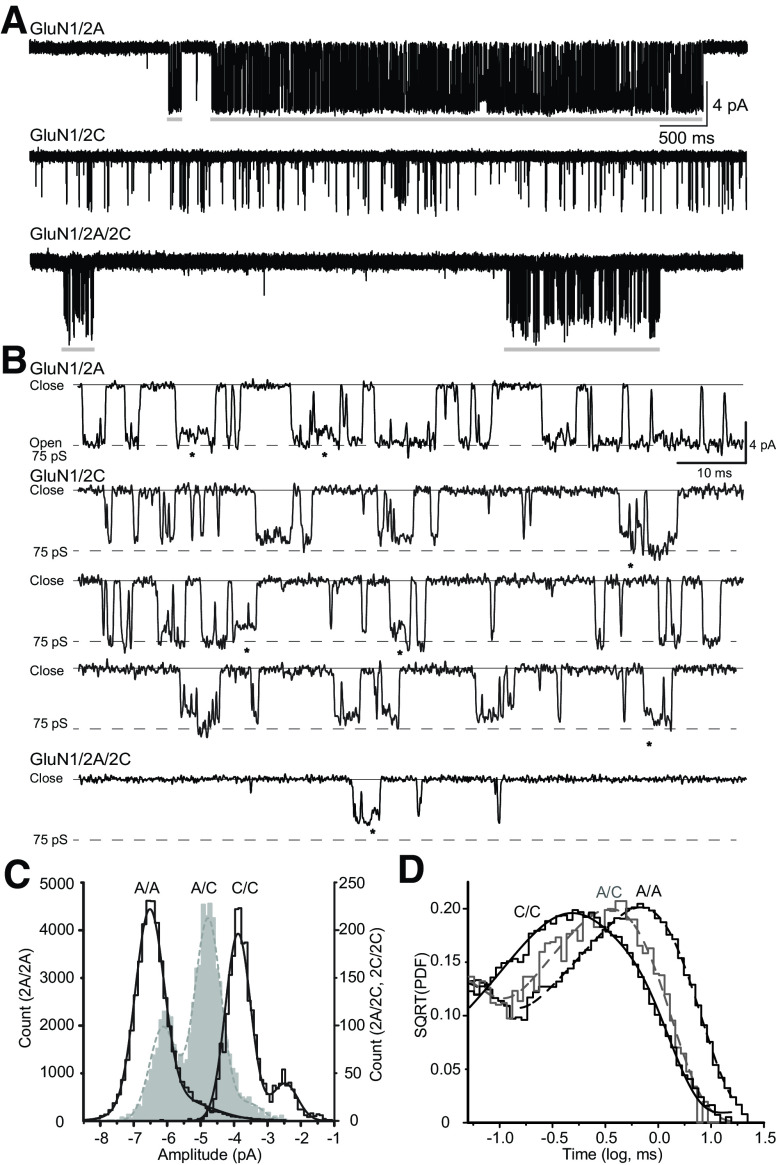
Fig. 17.
Single-channel properties of triheteromeric NMDA receptors. (A) Unitary currents for GluN1/2A, GluN1/2C, and GluN1/2A/2C NMDA receptors (VHOLD −80 mV). Openings of diheteromeric GluN1/2A and triheteromeric GluN1/2A/2C receptors are clustered into bursts (gray bars) separated by inactive periods. In contrast, openings of diheteromeric GluN1/2C receptors show no apparent burst structure. (B) Unitary currents in (A) are expanded to illustrate multiple conductance levels with direct sublevel transitions (asterisks). (C) Fitted amplitude histograms for GluN1/2A (left axis), GluN1/2A/2C (right axis), or GluN1/2C receptors (right axis) were fitted by the sum of 2–3 Gaussian distributions (smooth lines). (D) Representative open duration histograms for GluN1/2A, GluN1/2C, and GluN1/2A/2C receptors were fitted by multiple exponential components. Reproduced with permission from Bhattacharya et al. (2018).