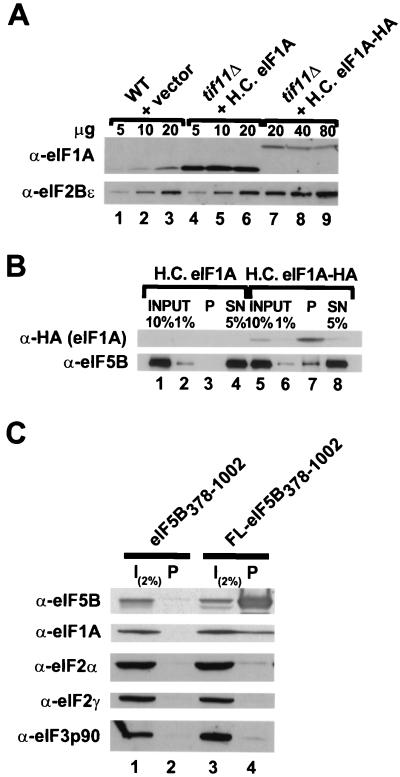
FIG. 6.
eIF5B and eIF1A interact in vivo. (A) Immunoblot analysis of eIF1A and eIF1A-HA expression. WCEs were prepared from the wild-type (WT) strain H1895 and derivatives of the isogenic tif11Δ strain H2809 containing the high-copy-number (H.C.) plasmid pDSO23 (TIF11 LEU2) encoding eIF1A or pDSO46 (TIF11-HA LEU2) encoding eIF1A-HA. The indicated amounts of WCEs were subjected to SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting using polyclonal antisera raised against yeast eIF2Bε (GCD6) or eIF1A. Immune complexes were visualized by ECL. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of eIF5B with epitope-tagged eIF1A. WCEs were prepared from the tif11Δ strains described for panel A, which express either eIF1A or HA epitope-tagged eIF1A (eIF1A-HA) from high-copy-number plasmids. Aliquots containing 800 μg of protein were incubated with monoclonal anti-HA antibodies (HA.11; Babco) prebound to protein A-Sepharose beads, and, after being washed, the bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-HA and anti-eIF5B antisera, as indicated. Input lanes contain 1 or 10% of the starting amount of WCE, the pellet lanes (P) containing 100% of the immunoprecipitated fraction, and the supernatant lanes (SN) contain 5% of the reaction mixtures following removal of the pellet. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of eIF1A with epitope-tagged eIF5B. WCEs were prepared from fun12Δ strain J111 expressing, from high-copy-number plasmids, eIF1A and either an untagged (pC1037) or FLAG epitope-tagged (FL; pC1007) form of N-terminally truncated eIF5B378–1002, as indicated. Aliquots containing 800 μg of protein were incubated with anti-FLAG affinity resin, and after being washed the bound proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using antisera specific for the proteins indicated at the left. The input (I) lanes containing 2% of the starting amount of WCE, and the pellet lanes contain the entire immunoprecipitated fraction.