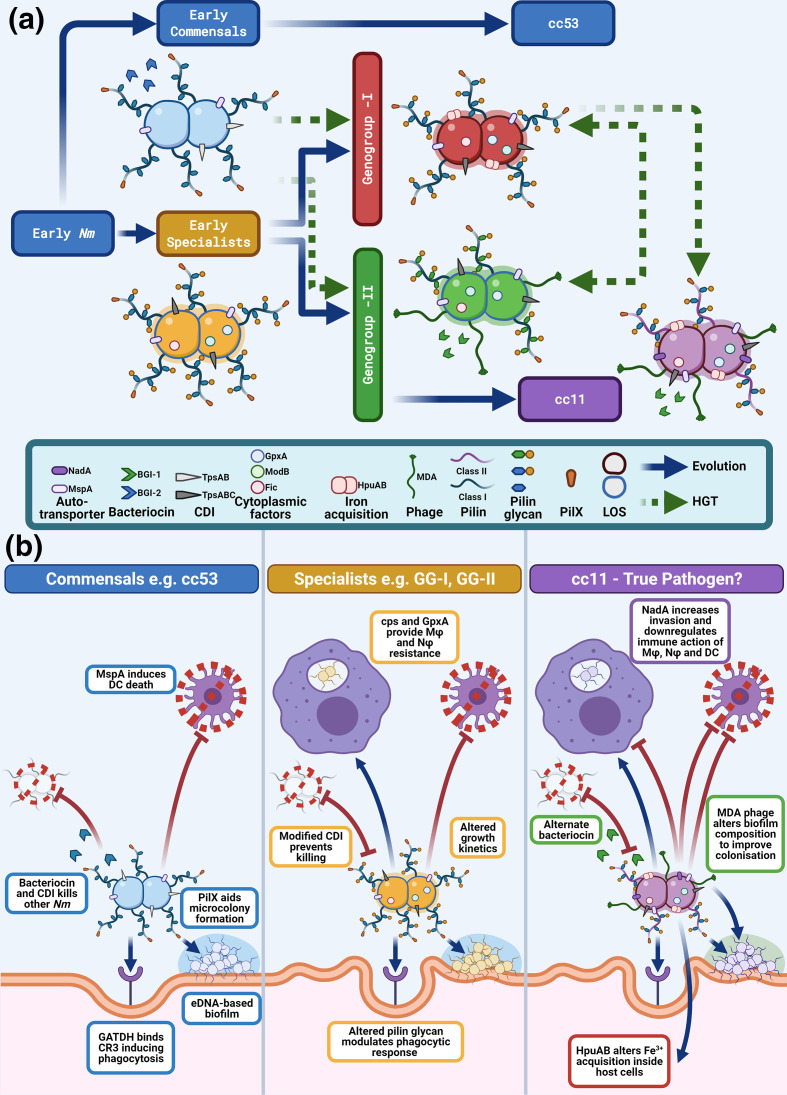
Fig. 7.
Putative biological functions of ancestral meningococci: commensals, early specialists and modern IMD lineage cc11. (a) Proposed stages in the evolution of the meningococcus. The early meningococcus, the commensal lineage (cc53, blue), an early specialist population (yellow node), GG-I (red), GG-II (green) and cc-11 (mauve). These colour codes correspond to the nodes in Fig. 5. Known virulence determinants are represented in the bottom panel by icons which appear in relationship to the cartoon representation of the meningococcus. Pilin glycan is represented by two different colour codes corresponding to: Hex(2-4)-GATDH O-linked glycan (blue) and O-acetyl-Hex (1-2) diNAcBac glycan (green). A yellow circle represents O-acetylation of the glycan. Type IV pili are shown as two classes: class I (blue) and II (purple). (b) Proposed interactions of cc53, early specialists and cc11 with host cells derived from the known functions of GIs enriched in each population (Fig. 5). Abbreviations: DC = dendritic cells, Mφ = macrophages, Nφ = neutrophils. Figure created using Biorender.com.