Figure 5. Surveillance and prevention of excessive R-loop formation.
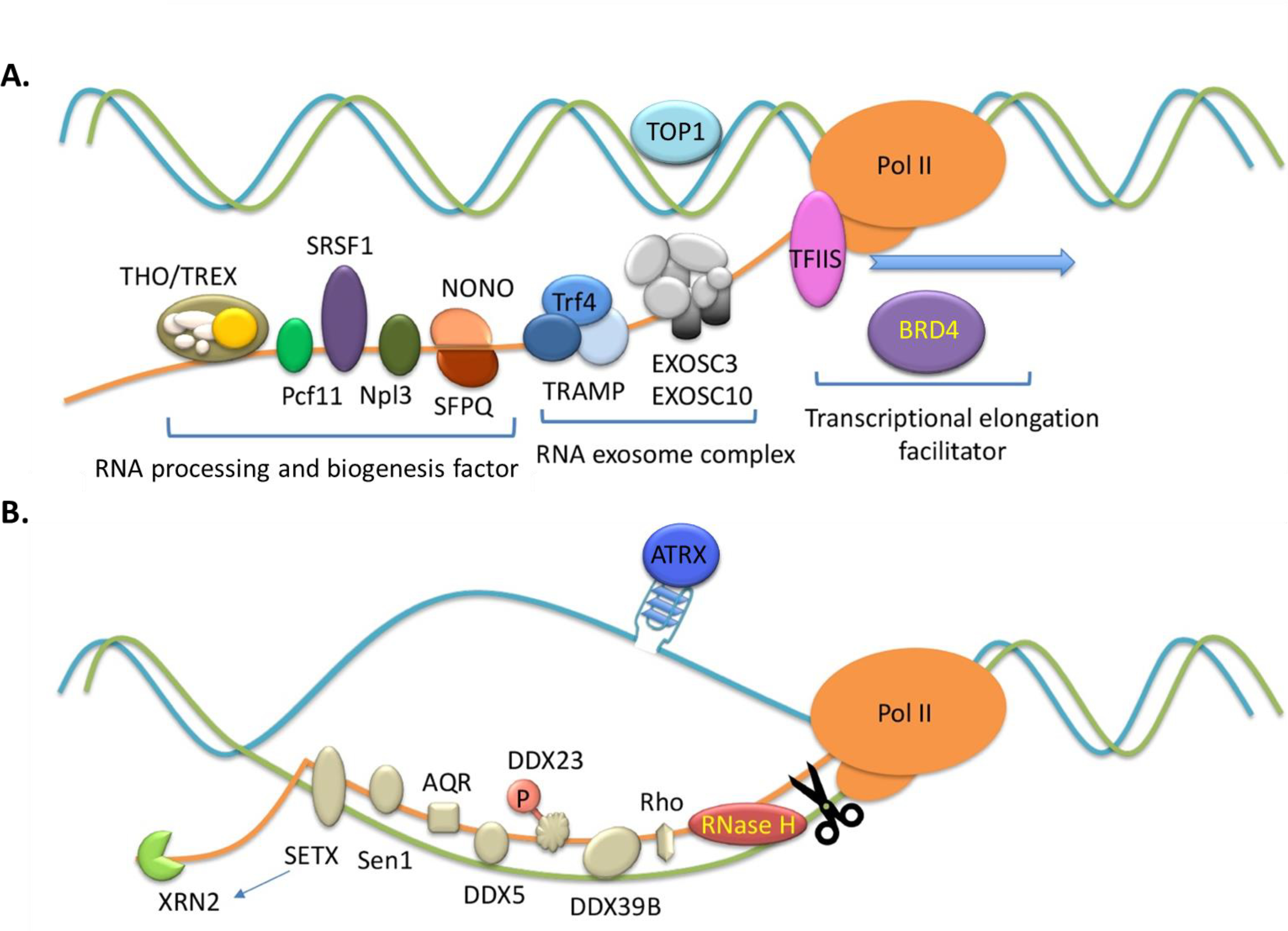
(A) R-loop formation is prevented by topoisomerase 1 (TOP1) as well as specific RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) such as SRSF1, the THO/TREX complex, Pcf11, Npl3, non-POU domain-containing octamer-binding protein (NONO) and Splicing factor proline- and glutamine-rich (SFPQ). RNA exosme complexes such as Trf4, exosome component 3 (EXOSC3) and exosome component 10 (EXOSC10), as well as transcription factor TFIIS and epigenetic reader Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) play roles in preventing R-loops.
(B) The removal of R-loops is mediated by RNase H and helicases such as senataxin (SETX), Sen1, aquarius (AQR), DDX5, DDX23, DDX39B and Rho. 5’−3’ exoribonuclease XRN2 cooperates with SETX or DDX5 to remove R-loops. ATRX at telomere may involved in resolving R-loops by suppressing deleterious DNA secondary structures.
