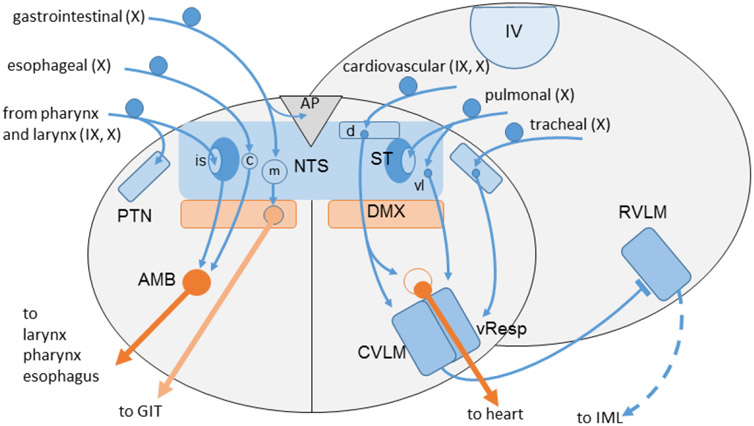
Fig. 5:
Schematic simplified summary of vagal (X) and glossopharyngeal (IX) afferent projections to the medulla oblongata and their major reflex connections to the dorsal motor nucleus (DMX), ambiguus nucleus (AMB; left: branchiomotor division; right: parasympathetic neurons of external formation) and the ventrolateral medulla. Note afferents from pharynx, larynx and trachea to the paratrigeminal nucleus (PTN). Arrows indicate excitatory (glutamatergic) connections; the bar on rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) symbolizes the inhibitory GABAergic projection from caudal ventrolateral medulla (CVLM) to glutamatergic presympathetic neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM). AP, area postrema; c, d, is, m, vl, central, dorsal, interstitial, medial, ventrolateral subnuclei of NTS; DMX, dorsal motor nucleus of vagus; IML, sympathetic intermediolateral nucleus; IV, fourth ventricle; vResp, ventral respiratory group; ST, solitary tract.