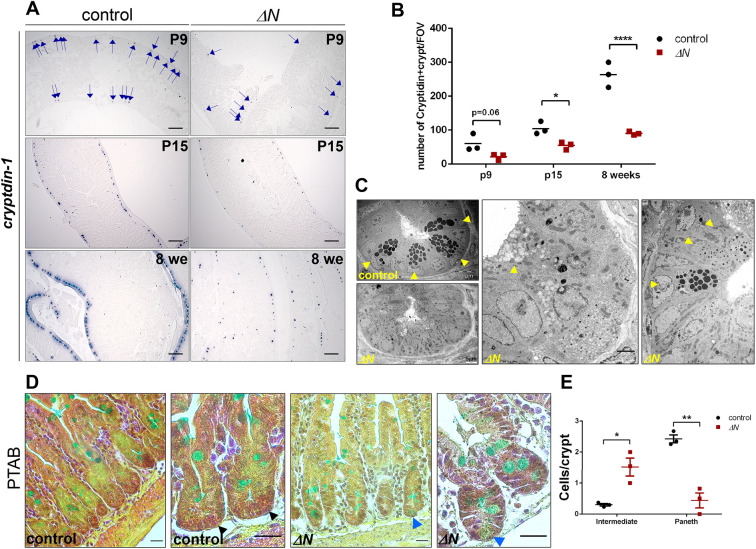
Fig. 5.
NF-κB is required for differentiation and maturation of Paneth cells. (A) ISH on PSI sections of control and ΔN mice (n=3/group) at P9, P15 and 8 weeks of age using a riboprobe for cryptdin-1. Blue arrows (P9 panels) point to cryptdin-1-positive cells. Scale bars: 200 µm. (B) Quantification of cryptdin-positive crypts in controls and ΔN mice at the indicated time points (n=3 per group). *P<0.05; ****P<0.0001 (two-way ANOVA). Error bars represent s.e.m. FOV, field of view. (C) TEM analysis of PSI crypts of ΔN and control mice (n=4 per group). Yellow arrowheads point to mature Paneth cells in control and immature intermediate cells in ΔN mice. Bottom left panel shows a ΔN crypt lacking Paneth cells. Scale bars: 10 µm (left, control); 5 µm (left, ΔN), 2 µm (middle, ΔN). (D) PTAB staining on PSI sections of ΔN and control mice (n=3 per group). Black arrowheads point to mature, lysozyme-containing Paneth cells (red granules) in controls, blue arrowheads to immature intermediate cells (blue-greenish) that lack lysozyme. Scale bars: 20 µm. (E) Quantification of immature intermediate cells versus mature Paneth cells in ΔN and control mice (n=3 per group). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (multiple t-test with Bonferroni correction). Error bars represent s.e.m.