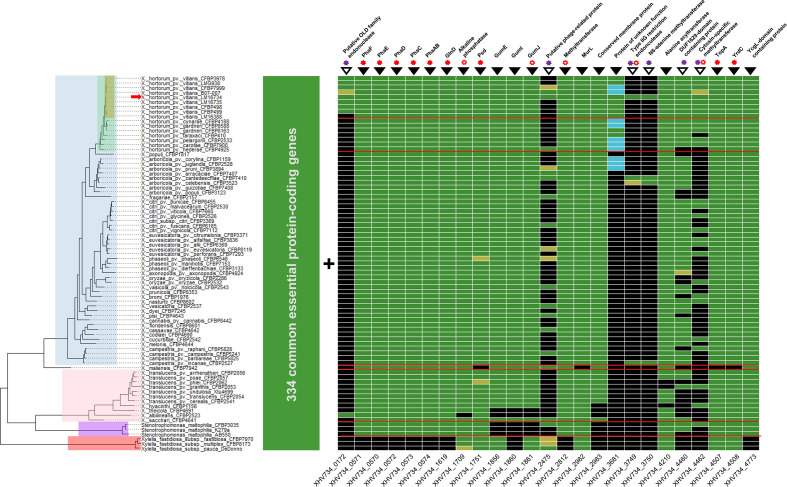
Fig. 3.
Conservation of the essential genes of X. hortorum pv. vitians LM16734 in the family Xanthomonadaceae . Colours on the phylogenetic tree indicate taxonomic levels: yellow = X. hortorum pv. vitians, green = X. hortorum , blue = Xanthomonas clade I, pink = Xanthomonas clade II, purple = Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, and red = Xylella fastidiosa . Taxonomic separations are also indicated by red lines on the gene conservation matrix. The position of the X.hortorum pv. vitians LM16734 genome in the phylogeny is highlighted by a red arrow. In the matrix, green boxes indicate detection with blastp (>50% coverage, >30% identity, e-value >10-5), yellow boxes detection with tblastn (> 50 % coverage, > 30 % identity, e-value > 10-5), and blue boxes detection with blastn (>50 % coverage, >70% identity, e-value >10-5). The numbers of gene loci are shown below the matrix, and gene product annotations are indicated above it. Empty and filled black inverted triangles refer to the two distribution patterns discussed in the text. Filled red asterisks indicate that at least one homologue was detected in the DEG10 v15.2 essential gene database with blastp (>50% coverage, >30% identity, e-value >10-5), while empty red asterisks indicate lower homology thresholds (>40% coverage and/or >20% identity and e-value >10-5). Finally, purple asterisks highlight the presence of mobile genetic-element-associated genes (transposase, integrase, reverse transcriptase) in the neighbourhood of the gene (<10 kb distance).